Page 289 - Centrifugal Pumps Design and Application
P. 289
258 Centrifugal Pumps: Design and Application
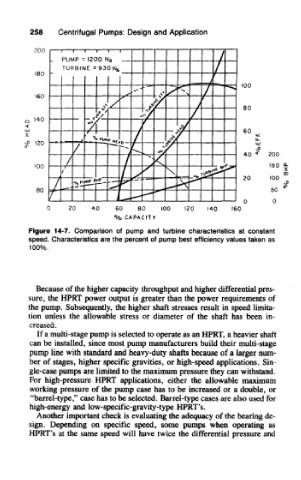
Figure 14-7. Comparison of pump and turbine characteristics at constant
speed. Characteristics are the percent of pump best efficiency values taken as
100%.
Because of the higher capacity throughput and higher differential pres-
sure, the HPRT power output is greater than the power requirements of
the pump. Subsequently, the higher shaft stresses result in speed limita-
tion unless the allowable stress or diameter of the shaft has been in-
creased.
If a multi-stage pump is selected to operate as an HPRT, a heavier shaft
can be installed, since most pump manufacturers build their multi-stage
pump line with standard and heavy-duty shafts because of a larger num-
ber of stages, higher specific gravities, or high-speed applications. Sin-
gle-case pumps are limited to the maximum pressure they can withstand.
For high-pressure HPRT applications, either the allowable maximum
working pressure of the pump case has to be increased or a double, or
"barrel-type," case has to be selected. Barrel-type cases are also used for
high-energy and low-specific-gravity-type HPRT's.
Another important check is evaluating the adequacy of the bearing de-
sign. Depending on specific speed, some pumps when operating as
HPRT's at the same speed will have twice the differential pressure and