Page 158 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 158
136 CORROSION CAUSES
Oil & gas
Pipelines Production Facilities
Natural Hazardous
gas liquids
2000K miles 156K miles
Transmission Transmission
300K miles 135K miles
Distribution
1700K miles Crude oil Liquid products
53K miles 82K miles
Gathering
28K miles Gathering
21K miles
1 mi = 1.61 km
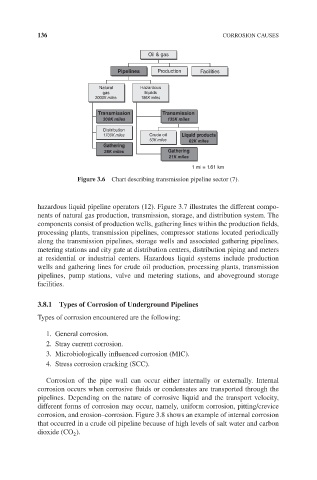
Figure 3.6 Chart describing transmission pipeline sector (7).
hazardous liquid pipeline operators (12). Figure 3.7 illustrates the different compo-
nents of natural gas production, transmission, storage, and distribution system. The
components consist of production wells, gathering lines within the production fields,
processing plants, transmission pipelines, compressor stations located periodically
along the transmission pipelines, storage wells and associated gathering pipelines,
metering stations and city gate at distribution centers, distribution piping and meters
at residential or industrial centers. Hazardous liquid systems include production
wells and gathering lines for crude oil production, processing plants, transmission
pipelines, pump stations, valve and metering stations, and aboveground storage
facilities.
3.8.1 Types of Corrosion of Underground Pipelines
Types of corrosion encountered are the following:
1. General corrosion.
2. Stray current corrosion.
3. Microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC).
4. Stress corrosion cracking (SCC).
Corrosion of the pipe wall can occur either internally or externally. Internal
corrosion occurs when corrosive fluids or condensates are transported through the
pipelines. Depending on the nature of corrosive liquid and the transport velocity,
different forms of corrosion may occur, namely, uniform corrosion, pitting/crevice
corrosion, and erosion–corrosion. Figure 3.8 shows an example of internal corrosion
that occurred in a crude oil pipeline because of high levels of salt water and carbon
dioxide (CO ).
2