Page 159 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 159
CORROSION OF UNDERGROUND PIPELINES 137
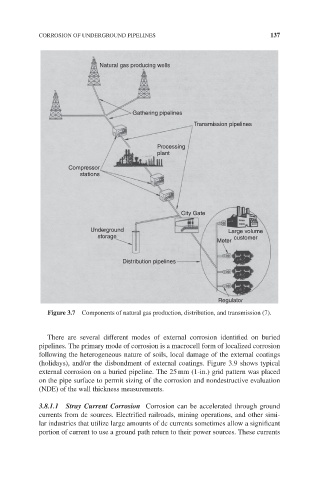
Natural gas producing wells
Gathering pipelines
Transmission pipelines
Processing
plant
Compressor
stations
City Gate
Underground Large volume
storage customer
Meter
Distribution pipelines
Regulator
Figure 3.7 Components of natural gas production, distribution, and transmission (7).
There are several different modes of external corrosion identified on buried
pipelines. The primary mode of corrosion is a macrocell form of localized corrosion
following the heterogeneous nature of soils, local damage of the external coatings
(holidays), and/or the disbondment of external coatings. Figure 3.9 shows typical
external corrosion on a buried pipeline. The 25 mm (1-in.) grid pattern was placed
on the pipe surface to permit sizing of the corrosion and nondestructive evaluation
(NDE) of the wall thickness measurements.
3.8.1.1 Stray Current Corrosion Corrosion can be accelerated through ground
currents from dc sources. Electrified railroads, mining operations, and other simi-
lar industries that utilize large amounts of dc currents sometimes allow a significant
portion of current to use a ground path return to their power sources. These currents