Page 298 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 298
276 CORROSION CONTROL AND PREVENTION
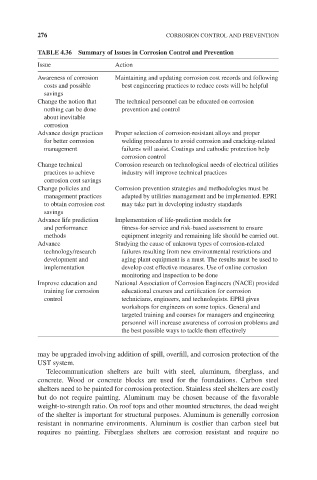
TABLE 4.36 Summary of Issues in Corrosion Control and Prevention
Issue Action
Awareness of corrosion Maintaining and updating corrosion cost records and following
costs and possible best engineering practices to reduce costs will be helpful
savings
Change the notion that The technical personnel can be educated on corrosion
nothing can be done prevention and control
about inevitable
corrosion
Advance design practices Proper selection of corrosion-resistant alloys and proper
for better corrosion welding procedures to avoid corrosion and cracking-related
management failures will assist. Coatings and cathodic protection help
corrosion control
Change technical Corrosion research on technological needs of electrical utilities
practices to achieve industry will improve technical practices
corrosion cost savings
Change policies and Corrosion prevention strategies and methodologies must be
management practices adapted by utilities management and be implemented. EPRI
to obtain corrosion cost may take part in developing industry standards
savings
Advance life prediction Implementation of life-prediction models for
and performance fitness-for-service and risk-based assessment to ensure
methods equipment integrity and remaining life should be carried out.
Advance Studying the cause of unknown types of corrosion-related
technology/research failures resulting from new environmental restrictions and
development and aging plant equipment is a must. The results must be used to
implementation develop cost effective measures. Use of online corrosion
monitoring and inspection to be done
Improve education and National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE) provided
training for corrosion educational courses and certification for corrosion
control technicians, engineers, and technologists. EPRI gives
workshops for engineers on some topics. General and
targeted training and courses for managers and engineering
personnel will increase awareness of corrosion problems and
the best possible ways to tackle them effectively
may be upgraded involving addition of spill, overfill, and corrosion protection of the
UST system.
Telecommunication shelters are built with steel, aluminum, fiberglass, and
concrete. Wood or concrete blocks are used for the foundations. Carbon steel
shelters need to be painted for corrosion protection. Stainless steel shelters are costly
but do not require painting. Aluminum may be chosen because of the favorable
weight-to-strength ratio. On roof tops and other mounted structures, the dead weight
of the shelter is important for structural purposes. Aluminum is generally corrosion
resistant in nonmarine environments. Aluminum is costlier than carbon steel but
requires no painting. Fiberglass shelters are corrosion resistant and require no