Page 33 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 33
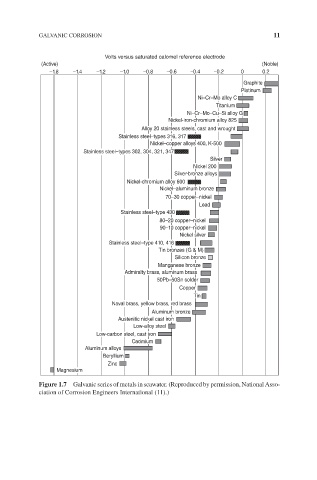
GALVANIC CORROSION 11
Volts versus saturated calomel reference electrode
(Active) (Noble)
–1.8 –1.4 –1.2 –1.0 –0.8 –0.6 –0.4 –0.2 0 0.2
Graphite
Platinum
Ni–Cr–Mo alloy C
Titanium
Ni–Cr–Mo–Cu–Si alloy G
Nickel-iron-chromium alloy 825
Alloy 20 stainless steels, cast and wrought
Stainless steel–types 316, 317
Nickel–copper alloys 400, K-500
Stainless steel–types 302, 304, 321, 347
Silver
Nickel 200
Silver-bronze alloys
Nickel-chromium alloy 600
Nickel–aluminum bronze
70–30 copper–nickel
Lead
Stainless steel–type 430
80–20 copper–nickel
90–10 copper–nickel
Nickel silver
Stainless steel–type 410, 416
Tin bronzes (G & M)
Silicon bronze
Manganese bronze
Admiralty brass, aluminum brass
50Pb–50Sn solder
Copper
Tin
Naval brass, yellow brass, red brass
Aluminum bronze
Austenitic nickel cast iron
Low-alloy steel
Low-carbon steel, cast iron
Cadmium
Aluminum alloys
Beryllium
Zinc
Magnesium
Figure 1.7 Galvanic series of metals in seawater. (Reproduced by permission, National Asso-
ciation of Corrosion Engineers International (11).)