Page 341 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 341
CORROSION STUDIES 319
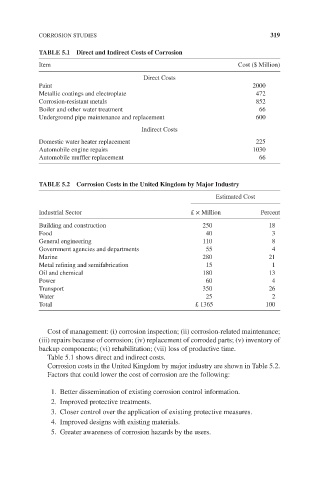
TABLE 5.1 Direct and Indirect Costs of Corrosion
Item Cost ($ Million)
Direct Costs
Paint 2000
Metallic coatings and electroplate 472
Corrosion-resistant metals 852
Boiler and other water treatment 66
Underground pipe maintenance and replacement 600
Indirect Costs
Domestic water heater replacement 225
Automobile engine repairs 1030
Automobile muffler replacement 66
TABLE 5.2 Corrosion Costs in the United Kingdom by Major Industry
Estimated Cost
Industrial Sector £ × Million Percent
Building and construction 250 18
Food 40 3
General engineering 110 8
Government agencies and departments 55 4
Marine 280 21
Metal refining and semifabrication 15 1
Oil and chemical 180 13
Power 60 4
Transport 350 26
Water 25 2
Total £ 1365 100
Cost of management: (i) corrosion inspection; (ii) corrosion-related maintenance;
(iii) repairs because of corrosion; (iv) replacement of corroded parts; (v) inventory of
backup components; (vi) rehabilitation; (vii) loss of productive time.
Table 5.1 shows direct and indirect costs.
Corrosion costs in the United Kingdom by major industry are shown in Table 5.2.
Factors that could lower the cost of corrosion are the following:
1. Better dissemination of existing corrosion control information.
2. Improved protective treatments.
3. Closer control over the application of existing protective measures.
4. Improved designs with existing materials.
5. Greater awareness of corrosion hazards by the users.