Page 135 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 135
Speight_Part II_B 11/7/01 3:11 PM Page 2.76
2.76 MANUFACTURE OF CHEMICALS
Regenerated
catalyst
Recycle hydrogen Hydrogen
Light ends
Regenerator Reactor Separator Separator or distillation
Separator
Spent catalyst
Platformate
Feedstock
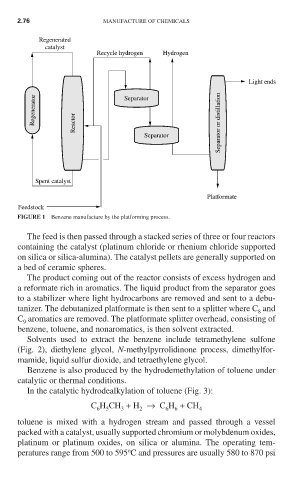
FIGURE 1 Benzene manufacture by the platforming process.
The feed is then passed through a stacked series of three or four reactors
containing the catalyst (platinum chloride or rhenium chloride supported
on silica or silica-alumina). The catalyst pellets are generally supported on
a bed of ceramic spheres.
The product coming out of the reactor consists of excess hydrogen and
a reformate rich in aromatics. The liquid product from the separator goes
to a stabilizer where light hydrocarbons are removed and sent to a debu-
tanizer. The debutanized platformate is then sent to a splitter where C and
8
C aromatics are removed. The platformate splitter overhead, consisting of
9
benzene, toluene, and nonaromatics, is then solvent extracted.
Solvents used to extract the benzene include tetramethylene sulfone
(Fig. 2), diethylene glycol, N-methylpyrrolidinone process, dimethylfor-
mamide, liquid sulfur dioxide, and tetraethylene glycol.
Benzene is also produced by the hydrodemethylation of toluene under
catalytic or thermal conditions.
In the catalytic hydrodealkylation of toluene (Fig. 3):
C H CH + H → C H + CH
6 5 3 2 6 6 4
toluene is mixed with a hydrogen stream and passed through a vessel
packed with a catalyst, usually supported chromium or molybdenum oxides,
platinum or platinum oxides, on silica or alumina. The operating tem-
o
peratures range from 500 to 595 C and pressures are usually 580 to 870 psi