Page 203 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 203
Speight_Part II_C 11/7/01 3:08 PM Page 2.143
CARBON 2.143
In the thermal black process, natural gas is cracked to carbon black and
o
hydrogen at 1100 to 1650 C in a refractory-lined furnace in a two-cycle
(heating and “making,” or decomposition) operation. The reaction is
CH → C + 2H
4 2
Yields of carbon are in the range 30 to 45 percent.
The gas furnace process, is similar to the oil furnace process but, like
the thermal black process, uses natural gas as feedstock.
Activated carbon is manufactured from carbonaceous materials, such as
petroleum coke, sawdust, lignite, coal, peat, wood, charcoal, nutshells, and
fruit pits. Activation is a physical change wherein the surface of the carbon
is increased by the removal of hydrocarbons by any one of several meth-
ods. The most widely used methods involve treatment of the carbonaceous
material with oxidizing gases such as air, steam, or carbon dioxide, and the
carbonization of the raw material in the presence of chemical agents such
as zinc chloride or phosphoric acid.
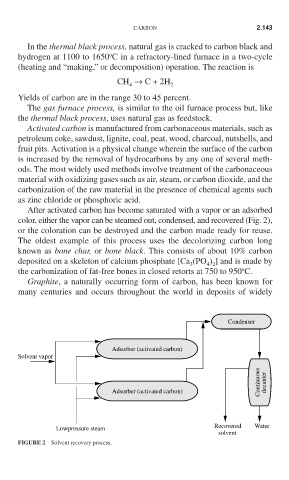
After activated carbon has become saturated with a vapor or an adsorbed
color, either the vapor can be steamed out, condensed, and recovered (Fig. 2),
or the coloration can be destroyed and the carbon made ready for reuse.
The oldest example of this process uses the decolorizing carbon long
known as bone char, or bone black. This consists of about 10% carbon
deposited on a skeleton of calcium phosphate [Ca (PO ) ] and is made by
4 2
3
o
the carbonization of fat-free bones in closed retorts at 750 to 950 C.
Graphite, a naturally occurring form of carbon, has been known for
many centuries and occurs throughout the world in deposits of widely
Condenser
Adsorber (activated carbon)
Solvent vapor
Continuous decanter
Adsorber (activated carbon)
Low-pressure steam Recovered Water
solvent
FIGURE 2 Solvent recovery process.