Page 22 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 22
Speight_Part 1_A 11/7/01 3:04 PM Page 1.8
1.8 REACTION TYPES
immersed in a molten salt bath. The nitrogen that accompanies the gener-
ated hydrogen is inert.
Amination is also achieved by the use of ammonia (NH ), in a process
3
referred to as ammonolysis. An example is the production of aniline
(C H NH ) from chlorobenzene (C H Cl) with ammonia (NH ). The reac-
5
3
6
5
6
2
tion proceeds only under high pressure.
The replacement of a nuclear substituent such as hydroxyl (–OH),
chloro, (–Cl), or sulfonic acid (–SO H) with amino (–NH ) by the use of
3
2
ammonia (ammonolysis) has been practiced for some time with feed-
stocks that have reaction-inducing groups present thereby making
replacement easier. For example, 1,4-dichloro-2-nitrobenzene can be
changed readily to 4-chloro-2-nitroaniline by treatment with aqueous
ammonia. Other molecules offer more processing difficulty, and pressure
vessels are required for the production of aniline from chlorobenzene or
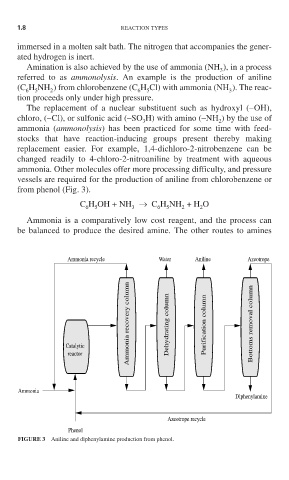
from phenol (Fig. 3).
C H OH + NH → C H NH + H O
6 5 3 6 5 2 2
Ammonia is a comparatively low cost reagent, and the process can
be balanced to produce the desired amine. The other routes to amines
Ammonia recycle Water Aniline Azeotrope
Ammonia recovery column Dehydrating column Purification column Bottoms removal column
Catalytic
reactor
Ammonia
Diphenylamine
Azeotrope recycle
Phenol
FIGURE 3 Aniline and diphenylamine production from phenol.