Page 41 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 41
Speight_Part 1_H 11/7/01 3:03 PM Page 1.27
HYDROFORMYLATION
The hydroformylation (oxo) reactions offer ways of converting a-olefins to
aldehydes and/or alcohols containing an additional carbon atom.
CH CH=CH + CO + H → CH CH CH CHO
3 2 2 3 2 2
CH CH CH CHO + H → CH CH CH CH OH
3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2
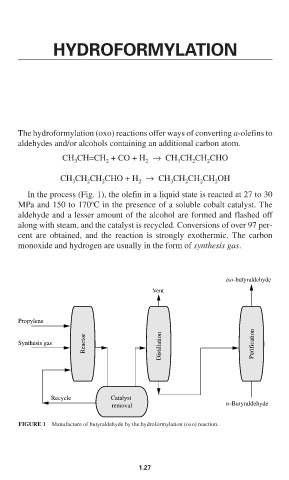
In the process (Fig. 1), the olefin in a liquid state is reacted at 27 to 30
o
MPa and 150 to 170 C in the presence of a soluble cobalt catalyst. The
aldehyde and a lesser amount of the alcohol are formed and flashed off
along with steam, and the catalyst is recycled. Conversions of over 97 per-
cent are obtained, and the reaction is strongly exothermic. The carbon
monoxide and hydrogen are usually in the form of synthesis gas.
iso-butyraldehyde
Vent
Propylene
Reactor Distillation Purification
Synthesis gas
Recycle Catalyst
removal n-Butyraldehyde
FIGURE 1 Manufacture of butyraldehyde by the hydroformylation (oxo) reaction.
1.27