Page 93 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 93
Speight_Part II_A 11/7/01 3:16 PM Page 2.34
ALKANOLAMINES
Alkanolamines are compounds that contain both the hydroxyl (alcoholic)
function (-OH) and the amino function (-NH ).
2
Ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, or butylene oxide react with ammonia to
produce alkanolamines. The more popular ethanolamines [NH (C H OH) ,
3-n 2 4 n
where n = 1,2,3: monoethanolamine, diethanolamine, and triethanolamine],
are derived from the reaction of ammonia with ethylene oxide.
Alkanolamines are manufactured from the corresponding oxide and
ammonia. Anhydrous or aqueous ammonia may be used, although
anhydrous ammonia is typically used to favor monoalkanolamine pro-
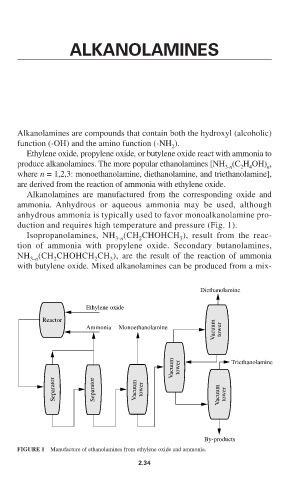
duction and requires high temperature and pressure (Fig. 1).
Isopropanolamines, NH (CH CHOHCH ), result from the reac-
3-n 2 3
tion of ammonia with propylene oxide. Secondary butanolamines,
NH (CH CHOHCH CH ), are the result of the reaction of ammonia
3-n 2 2 3
with butylene oxide. Mixed alkanolamines can be produced from a mix-
Diethanolamine
Ethylene oxide
Reactor
Vacuum tower
Ammonia Monoethanolamine
Vacuum tower Triethanolamine
Separator Separator Vacuum tower Vacuum tower
By-products
FIGURE 1 Manufacture of ethanolamines from ethylene oxide and ammonia.
2.34