Page 353 - Chemical engineering design
P. 353
328
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
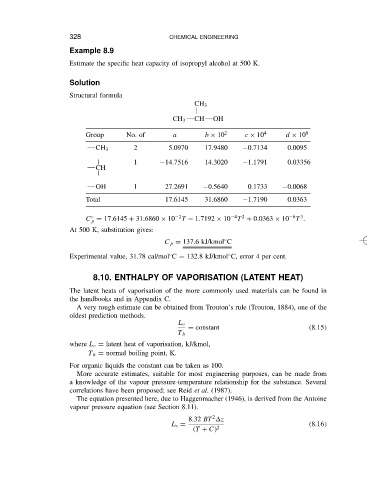
Example 8.9
Estimate the specific heat capacity of isopropyl alcohol at 500 K.
Solution
Structural formula
CH 3
CH 3 CH OH
Group No. of a b ð 10 2 c ð 10 4 d ð 10 6
2 5.0970 17.9480 0.7134 0.0095
CH 3
1 14.7516 14.3020 1.1791 0.03356
CH
OH 1 27.2691 0.5640 0.1733 0.0068
Total 17.6145 31.6860 1.7190 0.0363
4 2
2
3
6
Ž
C D 17.6145 C 31.6860 ð 10 T 1.7192 ð 10 T C 0.0363 ð 10 T .
p
At 500 K, substitution gives:
Ž
C p D 137.6 kJ/kmol C
Ž
Ž
Experimental value, 31.78 cal/mol C D 132.8 kJ/kmol C, error 4 per cent.
8.10. ENTHALPY OF VAPORISATION (LATENT HEAT)
The latent heats of vaporisation of the more commonly used materials can be found in
the handbooks and in Appendix C.
A very rough estimate can be obtained from Trouton’s rule (Trouton, 1884), one of the
oldest prediction methods.
L v
D constant 8.15
T b
where L v D latent heat of vaporisation, kJ/kmol,
T b D normal boiling point, K.
For organic liquids the constant can be taken as 100.
More accurate estimates, suitable for most engineering purposes, can be made from
a knowledge of the vapour pressure-temperature relationship for the substance. Several
correlations have been proposed; see Reid et al. (1987).
The equation presented here, due to Haggenmacher (1946), is derived from the Antoine
vapour pressure equation (see Section 8.11).
2
8.32 BT z
L v D 8.16
T C C 2