Page 351 - Chemical engineering design
P. 351
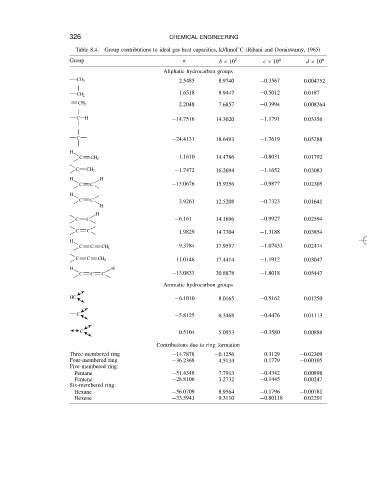
326
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Table 8.4.
a
2
Group Group contributions to ideal gas heat capacities, kJ/kmol ° C (Rihani and Doraiswamy, 1965) 6
4
c ð 10
d ð 10
b ð 10
Aliphatic hydrocarbon groups
CH 3 2.5485 8.9740 0.3567 0.004752
1.6518 8.9447 0.5012 0.0187
CH 2
CH 2 2.2048 7.6857 0.3994 0.008264
C H 14.7516 14.3020 1.1791 0.03356
C 24.4131 18.6493 1.7619 0.05288
H
C CH 2 1.1610 14.4786 0.8031 0.01792
C CH 2 1.7472 16.2694 1.1652 0.03083
H H
C C 13.0676 15.9356 0.9877 0.02305
H
C C 3.9261 12.5208 0.7323 0.01641
H
H
C C 6.161 14.1696 0.9927 0.02594
C C 1.9829 14.7304 1.3188 0.03854
H
C C CH 2 9.3784 17.9597 1.07433 0.02474
C C CH 2 11.0146 17.4414 1.1912 0.03047
H H
C C C 13.0833 20.8878 1.8018 0.05447
Aromatic hydrocarbon groups
HC 6.1010 8.0165 0.5162 0.01250
C 5.8125 6.3468 0.4476 0.01113
C 0.5104 5.0953 0.3580 0.00888
Contributions due to ring formation
Three-membered ring 14.7878 0.1256 0.3129 0.02309
Four-membered ring 36.2368 4.5134 0.1779 0.00105
Five-membered ring:
Pentane 51.4348 7.7913 0.4342 0.00898
Pentene 28.8106 3.2732 0.1445 0.00247
Six-membered ring:
Hexane 56.0709 8.9564 0.1796 0.00781
Hexene 33.5941 9.3110 0.80118 0.02291