Page 349 - Chemical engineering design
P. 349
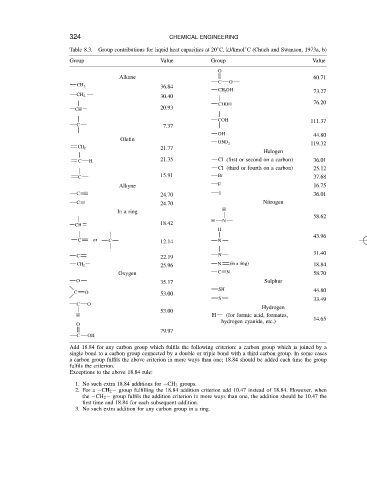
324
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Table 8.3.
Value
Value
Group
Group Group contributions for liquid heat capacities at 20 ° C, kJ/kmol ° C (Chueh and Swanson, 1973a, b)
O
Alkane 60.71
C O
36.84
CH 3
CH 2 OH 73.27
30.40
CH 2
CHOH 76.20
CH 20.93
COH 111.37
C 7.37
OH 44.80
Olefin
ONO 2 119.32
CH 2 21.77
Halogen
C H 21.35 Cl (first or second on a carbon) 36.01
Cl (third or fourth on a carbon) 25.12
C 15.91 Br 37.68
Alkyne F 16.75
CH 24.70 I 36.01
C 24.70 Nitrogen
H
In a ring
58.62
H N
CH 18.42
H
43.96
C or C 12.14 N
C 22.19 N 31.40
25.96
CH 2 N (in a ring) 18.84
Oxygen C N 58.70
O 35.17 Sulphur
SH
C O 53.00 44.80
S 33.49
C O
Hydrogen
53.00
H H (for formic acid, formates,
hydrogen cyanide, etc.) 14.65
O
79.97
C OH
Add 18.84 for any carbon group which fulfils the following criterion: a carbon group which is joined by a
single bond to a carbon group connected by a double or triple bond with a third carbon group. In some cases
a carbon group fulfils the above criterion in more ways than one; 18.84 should be added each time the group
fulfils the criterion.
Exceptions to the above 18.84 rule:
1. No such extra 18.84 additions for CH 3 groups.
2. For a CH 2 group fulfilling the 18.84 addition criterion add 10.47 instead of 18.84. However, when
the CH 2 group fulfils the addition criterion in more ways than one, the addition should be 10.47 the
first time and 18.84 for each subsequent addition.
3. No such extra addition for any carbon group in a ring.