Page 372 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 372
Separator Design 351
m) in diameter and 20 ft (6.70 m) high. These data can be use as a guide to esti-
mate the motor power.
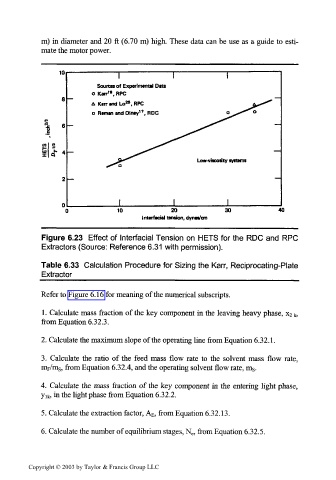
10
I I
Sources of Experimental Dita
O Karr'*, RFC
25
A Karr and Lo , RFC
17
a Reman and Olney , RDC
s R
j: 6
4
Low-vucoilty systems
10 20 30 40
Intel-facial tension, dynes/cm
Figure 6.23 Effect of Intel-facial Tension on NETS for the RDC and RFC
Extractors (Source: Reference 6.31 with permission).
Table 6.33 Calculation Procedure for Sizing the Karr, Reciprocating-Plate
Extractor____________________________________
Refer to Figure 6.16 for meaning of the numerical subscripts.
1. Calculate mass fraction of the key component in the leaving heavy phase, x k,
2
from Equation 6.32.3.
2. Calculate the maximum slope of the operating line from Equation 6.32.1.
3. Calculate the ratio of the feed mass flow rate to the solvent mass flow rate,
m F/m s, from Equation 6.32.4, and the operating solvent flow rate, m s.
4. Calculate the mass fraction of the key component in the entering light phase,
yik, in the light phase from Equation 6.32.2.
5. Calculate the extraction factor, A E, from Equation 6.32.13.
6. Calculate the number of equilibrium stages, N, from Equation 6.32.5.
e
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC