Page 202 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 202
180 6 Enantiomer Separations using Designed Imprinted Chiral Phases
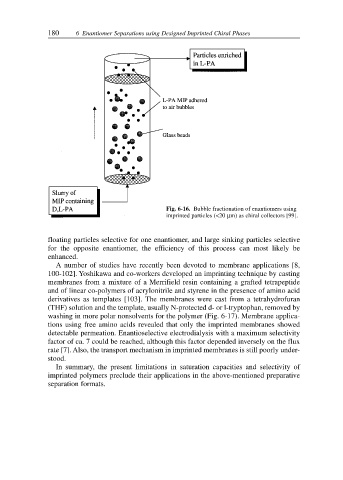
Fig. 6-16. Bubble fractionation of enantiomers using
imprinted particles (<20 µm) as chiral collectors [99].
floating particles selective for one enantiomer, and large sinking particles selective
for the opposite enantiomer, the efficiency of this process can most likely be
enhanced.
A number of studies have recently been devoted to membrane applications [8,
100-102]. Yoshikawa and co-workers developed an imprinting technique by casting
membranes from a mixture of a Merrifield resin containing a grafted tetrapeptide
and of linear co-polymers of acrylonitrile and styrene in the presence of amino acid
derivatives as templates [103]. The membranes were cast from a tetrahydrofuran
(THF) solution and the template, usually N-protected d- or l-tryptophan, removed by
washing in more polar nonsolvents for the polymer (Fig. 6-17). Membrane applica-
tions using free amino acids revealed that only the imprinted membranes showed
detectable permeation. Enantioselective electrodialysis with a maximum selectivity
factor of ca. 7 could be reached, although this factor depended inversely on the flux
rate [7]. Also, the transport mechanism in imprinted membranes is still poorly under-
stood.
In summary, the present limitations in saturation capacities and selectivity of
imprinted polymers preclude their applications in the above-mentioned preparative
separation formats.