Page 199 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 199
6.7 Methods for Combinatorial Synthesis and Sreening of Large Numbers of MIP 177
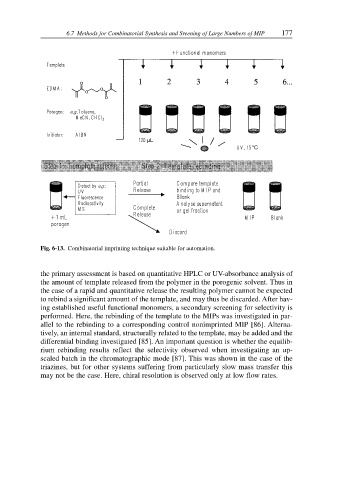
Fig. 6-13. Combinatorial imprinting technique suitable for automation.
the primary assessment is based on quantitative HPLC or UV-absorbance analysis of
the amount of template released from the polymer in the porogenic solvent. Thus in
the case of a rapid and quantitative release the resulting polymer cannot be expected
to rebind a significant amount of the template, and may thus be discarded. After hav-
ing established useful functional monomers, a secondary screening for selectivity is
performed. Here, the rebinding of the template to the MIPs was investigated in par-
allel to the rebinding to a corresponding control nonimprinted MIP [86]. Alterna-
tively, an internal standard, structurally related to the template, may be added and the
differential binding investigated [85]. An important question is whether the equilib-
rium rebinding results reflect the selectivity observed when investigating an up-
scaled batch in the chromatographic mode [87]. This was shown in the case of the
triazines, but for other systems suffering from particularly slow mass transfer this
may not be the case. Here, chiral resolution is observed only at low flow rates.