Page 198 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 198
176 6 Enantiomer Separations using Designed Imprinted Chiral Phases
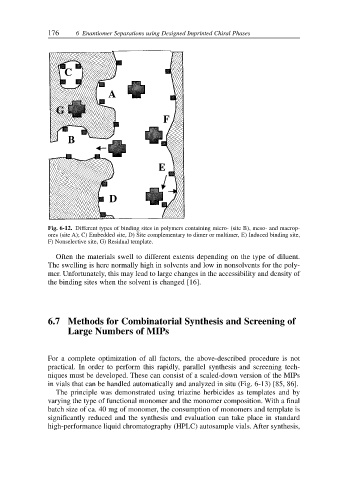
Fig. 6-12. Different types of binding sites in polymers containing micro- (site B), meso- and macrop-
ores (site A); C) Embedded site, D) Site complementary to dimer or multimer, E) Induced binding site,
F) Nonselective site, G) Residual template.
Often the materials swell to different extents depending on the type of diluent.
The swelling is here normally high in solvents and low in nonsolvents for the poly-
mer. Unfortunately, this may lead to large changes in the accessibility and density of
the binding sites when the solvent is changed [16].
6.7 Methods for Combinatorial Synthesis and Screening of
Large Numbers of MIPs
For a complete optimization of all factors, the above-described procedure is not
practical. In order to perform this rapidly, parallel synthesis and screening tech-
niques must be developed. These can consist of a scaled-down version of the MIPs
in vials that can be handled automatically and analyzed in situ (Fig. 6-13) [85, 86].
The principle was demonstrated using triazine herbicides as templates and by
varying the type of functional monomer and the monomer composition. With a final
batch size of ca. 40 mg of monomer, the consumption of monomers and template is
significantly reduced and the synthesis and evaluation can take place in standard
high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) autosample vials. After synthesis,