Page 427 - Civil Engineering Formulas
P. 427
HYDRAULICS AND WATERWORKS FORMULAS 353
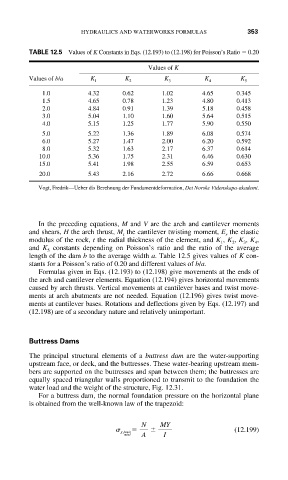
TABLE 12.5 Values of K Constants in Eqs. (12.193) to (12.198) for Poisson’s Ratio 0.20
Values of K
Values of b/a K 1 K 2 K 3 K 4 K 5
1.0 4.32 0.62 1.02 4.65 0.345
1.5 4.65 0.78 1.23 4.80 0.413
2.0 4.84 0.91 1.39 5.18 0.458
3.0 5.04 1.10 1.60 5.64 0.515
4.0 5.15 1.25 1.77 5.90 0.550
5.0 5.22 1.36 1.89 6.08 0.574
6.0 5.27 1.47 2.00 6.20 0.592
8.0 5.32 1.63 2.17 6.37 0.614
10.0 5.36 1.75 2.31 6.46 0.630
15.0 5.41 1.98 2.55 6.59 0.653
20.0 5.43 2.16 2.72 6.66 0.668
Vogt, Fredrik—Ueber dis Berehnung der Fundamentdeformation, Det Norske Videnskapa-akademi.
In the preceding equations, M and V are the arch and cantilever moments
and shears, H the arch thrust, M the cantilever twisting moment, E the elastic
t
r
modulus of the rock, t the radial thickness of the element, and K , K , K , K ,
3
4
2
1
and K constants depending on Poisson’s ratio and the ratio of the average
5
length of the dam b to the average width a. Table 12.5 gives values of K con-
stants for a Poisson’s ratio of 0.20 and different values of b/a.
Formulas given in Eqs. (12.193) to (12.198) give movements at the ends of
the arch and cantilever elements. Equation (12.194) gives horizontal movements
caused by arch thrusts. Vertical movements at cantilever bases and twist move-
ments at arch abutments are not needed. Equation (12.196) gives twist move-
ments at cantilever bases. Rotations and deflections given by Eqs. (12.197) and
(12.198) are of a secondary nature and relatively unimportant.
Buttress Dams
The principal structural elements of a buttress dam are the water-supporting
upstream face, or deck, and the buttresses. These water-bearing upstream mem-
bers are supported on the buttresses and span between them; the buttresses are
equally spaced triangular walls proportioned to transmit to the foundation the
water load and the weight of the structure, Fig. 12.31.
For a buttress dam, the normal foundation pressure on the horizontal plane
is obtained from the well-known law of the trapezoid:
N MY
(12.199)
x max
min A I