Page 136 - Color Atlas of Biochemistry
P. 136
Energy Metabolism 127
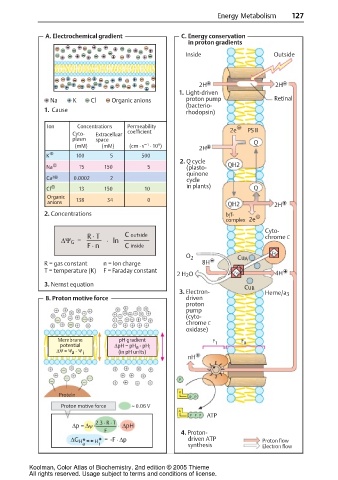
A. Electrochemical gradient C. Energy conservation
in proton gradients
Inside Outside
2H 2H
1. Light-driven
Na K Cl Organic anions proton pump Retinal
(bacterio-
1. Cause rhodopsin)
Ion Concentrations Permeability
Cyto- Extracelluar coefficient 2e PS II
plasm space Q
9
–1
(mM) (mM) (cm · s · 10 ) 2H
K 100 5 500
2. Q cycle
Na 15 150 5 (plasto- QH2
quinone
Ca 2 0.0002 2 cycle
in plants)
Cl 13 150 10 Q
Organic
anions 138 34 0 QH2 2H
2. Concentrations b/f-
complex 2e
Cyto-
R · T C outside chrome C
∆Ψ G = · ln
F · n C inside
Fe
O 2 CuA
R = gas constant n = Ion charge 8H
T = temperature (K) F = Faraday constant
2 H 2 O Fe 4H
3. Nernst equation
CuB
3. Electron- Heme/a 3
B. Proton motive force driven
proton
pump
(cyto-
chrome C
oxidase)
Membrane pH gradient F F
potential ∆pH = pH - pH i 1 0
a
∆ ψ = ψ - ψ i (in pH units)
a
nH
P
A
Protein
P P
Proton motive force ≈ 0.06 V
A
PP P ATP
2.3 · R · T
∆p = ∆ψ - · ∆pH
F 4. Proton-
∆G = -F · ∆p driven ATP Proton flow
H
H
a i synthesis Electron flow
Koolman, Color Atlas of Biochemistry, 2nd edition © 2005 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.