Page 372 - Color Atlas of Biochemistry
P. 372
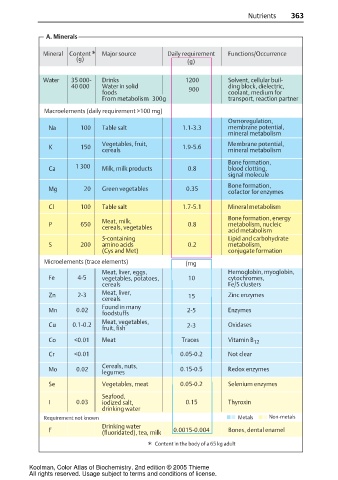
Nutrients 363
A. Minerals
Mineral Content * Major source Daily requirement Functions/Occurrence
(g) (g)
Water 35 000- Drinks 1200 Solvent, cellular buil-
40 000 Water in solid 900 ding block, dielectric,
foods coolant, medium for
From metabolism 300g transport, reaction partner
Macroelements (daily requirement >100 mg)
Osmoregulation,
Na 100 Table salt 1.1-3.3 membrane potential,
mineral metabolism
Vegetables, fruit, Membrane potential,
K 150 1.9-5.6
cereals mineral metabolism
Bone formation,
Ca 1 300 Milk, milk products 0.8 blood clotting,
signal molecule
Bone formation,
Mg 20 Green vegetables 0.35
cofactor for enzymes
Cl 100 Table salt 1.7-5.1 Mineral metabolism
Bone formation, energy
Meat, milk,
P 650 0.8 metabolism, nucleic
cereals, vegetables
acid metabolism
S-containing Lipid and carbohydrate
S 200 amino acids 0.2 metabolism,
(Cys and Met) conjugate formation
Microelements (trace elements) (mg
Meat, liver, eggs, Hemoglobin, myoglobin,
Fe 4-5 vegetables, potatoes, 10 cytochromes,
cereals Fe/S clusters
Meat, liver,
Zn 2-3 15 Zinc enzymes
cereals
Found in many
Mn 0.02 2-5 Enzymes
foodstuffs
Meat, vegetables,
Cu 0.1-0.2 2-3 Oxidases
fruit, fish
Co <0.01 Meat Traces Vitamin B 12
Cr <0.01 0.05-0.2 Not clear
Cereals, nuts,
Mo 0.02 0.15-0.5 Redox enzymes
legumes
Se Vegetables, meat 0.05-0.2 Selenium enzymes
Seafood,
I 0.03 iodized salt, 0.15 Thyroxin
drinking water
Requirement not known Metals Non-metals
Drinking water
F (fluoridated), tea, milk 0.0015-0.004 Bones, dental enamel
* Content in the body of a 65 kg adult
Koolman, Color Atlas of Biochemistry, 2nd edition © 2005 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.