Page 79 - Compact Numerical Methods For Computers
P. 79
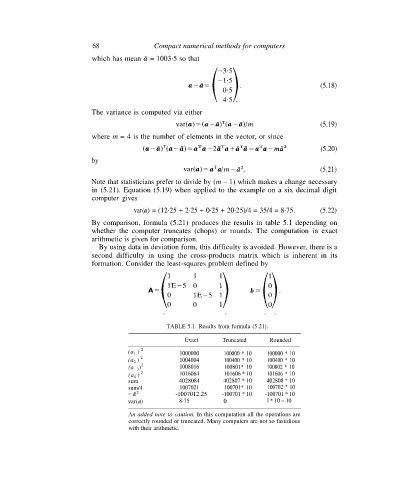
68 Compact numerical methods for computers
which has mean = 1003·5 so that
(5.18)
The variance is computed via either
(5.19)
where m = 4 is the number of elements in the vector, or since
(5.20)
by
(5.21)
Note that statisticians prefer to divide by (m – 1) which makes a change necessary
in (5.21). Equation (5.19) when applied to the example on a six decimal digit
computer gives
var(a) = (12·25 + 2·25 + 0·25 + 20·25)/4 = 35/4 = 8·75. (5.22)
By comparison, formula (5.21) produces the results in table 5.1 depending on
whether the computer truncates (chops) or rounds. The computation in exact
arithmetic is given for comparison.
By using data in deviation form, this difficulty is avoided. However, there is a
second difficulty in using the cross-products matrix which is inherent in its
formation. Consider the least-squares problem defined by
TABLE 5.1. Results from formula (5.21).
Exact Truncated Rounded
(a 1 ) 2 1000000 100000 * 10 100000 * 10
(a 2 ) 2 1004004 100400 * 10 100400 * 10
(a 3 ) 2 1008016 100801* 10 100802 * 10
2 1016064 101606 * 10 101606 * 10
(a 4 )
sum 4028084 402807 * 10 402808 * 10
sum/4 1007021 100701* 10 100702 * 10
-1007012.25 -100701 * 10 -100701 * 10
var(a) 8·75 0 l * 10 = 10
An added note to caution. In this computation all the operations are
correctly rounded or truncated. Many computers are not so fastidious
with their arithmetic.