Page 216 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 216
Reciprocating Compressors Chapter 5 205
drop as that through a compressor valve when flowing the same quantity of the
same gas at the same pressure and temperature. Compressor and compressor
valve manufacturers will use either term (resistance factor or VEA) to describe
the relative efficiency of a compressor valve. One can be converted into the other:
2
A VLV PKT ð A VLV PKT Þ
VEA ¼ p or R P ¼
2
ffiffiffiffiffiffi
R P ð VEAÞ
Some further discussion about the “S RPM” term in the above relation-
ships is required. This term is generally known as piston speed, or the average
linear speed at which the piston moves through one stroke length. Average pis-
ton speed in feet per minute is calculated by:
2 S RPM S RPM
PS ¼ ,or PS ¼
12 6
where
PS¼piston speed, feet per minute
S ¼stroke, in
RPM¼rotating speed, rpm
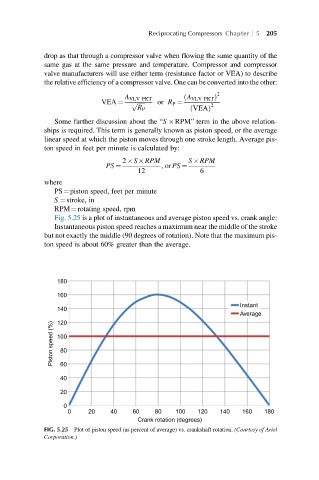
Fig. 5.25 is a plot of instantaneous and average piston speed vs. crank angle:
Instantaneous piston speed reaches a maximum near the middle of the stroke
but not exactly the middle (90 degrees of rotation). Note that the maximum pis-
ton speed is about 60% greater than the average.
180
160
Instant
140
Average
Piston speed (%) 100
120
80
60
40
20
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
Crank rotation (degrees)
FIG. 5.25 Plot of piston speed (as percent of average) vs. crankshaft rotation. (Courtesy of Ariel
Corporation.)