Page 256 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 256
Reciprocating Compressors Chapter 5 241
4
Dynamic torque Maximum allowable stress and computed combined stress
× 10
15 12,000
Design factor = 1.5
Coupling
Design factor = 1.5
10,000
Design factor = 2.0
10 8000
Design factor = 2.0
in-lbs (pk) psi (pk) 6000
5 4000
2000
0
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 0 5 10 15 20 25
Field Field
Compressor Motor Compressor Motor
Dynamic torque distribution Dynamic stress distribution
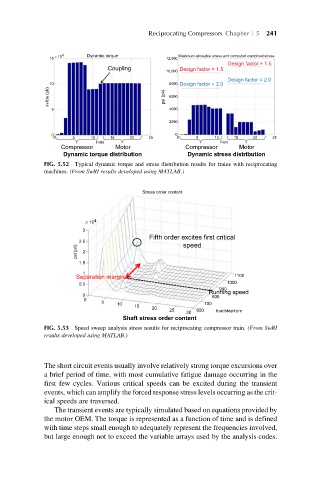
FIG. 5.52 Typical dynamic torque and stress distribution results for trains with reciprocating
machines. (From SwRI results developed using MATLAB.)
Stress order content
× 10 4
3
Fifth order excites first critical
2.5
psi (pk) 2 speed
1.5
1
1100
Separation margin
1000
0.5
900
Running speed
0
800
0
5
10 700
15
20
25 600
loadstep/rpm
30
Shaft stress order content
FIG. 5.53 Speed sweep analysis stress results for reciprocating compressor train. (From SwRI
results developed using MATLAB.)
The short circuit events usually involve relatively strong torque excursions over
a brief period of time, with most cumulative fatigue damage occurring in the
first few cycles. Various critical speeds can be excited during the transient
events, which can amplify the forced response stress levels occurring as the crit-
ical speeds are traversed.
The transient events are typically simulated based on equations provided by
the motor OEM. The torque is represented as a function of time and is defined
with time steps small enough to adequately represent the frequencies involved,
but large enough not to exceed the variable arrays used by the analysis codes.