Page 398 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 398
376 SECTION III Applications
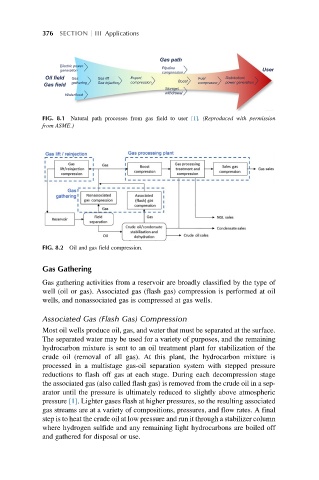
Gas path
Electric power Pipeline
generation compression User
Oil field Gas Gas lift Export Fuel Distribution/
gathering Gas injection compression Boost compressor power generation
Gas field
Storage/
withdrawal
Waterflood
FIG. 8.1 Natural path processes from gas field to user [1]. (Reproduced with permission
from ASME.)
FIG. 8.2 Oil and gas field compression.
Gas Gathering
Gas gathering activities from a reservoir are broadly classified by the type of
well (oil or gas). Associated gas (flash gas) compression is performed at oil
wells, and nonassociated gas is compressed at gas wells.
Associated Gas (Flash Gas) Compression
Most oil wells produce oil, gas, and water that must be separated at the surface.
The separated water may be used for a variety of purposes, and the remaining
hydrocarbon mixture is sent to an oil treatment plant for stabilization of the
crude oil (removal of all gas). At this plant, the hydrocarbon mixture is
processed in a multistage gas-oil separation system with stepped pressure
reductions to flash off gas at each stage. During each decompression stage
the associated gas (also called flash gas) is removed from the crude oil in a sep-
arator until the pressure is ultimately reduced to slightly above atmospheric
pressure [1]. Lighter gases flash at higher pressures, so the resulting associated
gas streams are at a variety of compositions, pressures, and flow rates. A final
step is to heat the crude oil at low pressure and run it through a stabilizer column
where hydrogen sulfide and any remaining light hydrocarbons are boiled off
and gathered for disposal or use.