Page 107 - Computational Modeling in Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics
P. 107
96 Computational Modeling in Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics
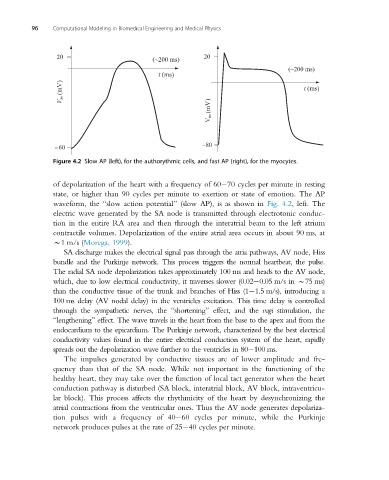
Figure 4.2 Slow AP (left), for the authorythmic cells, and fast AP (right), for the myocytes.
of depolarization of the heart with a frequency of 60 70 cycles per minute in resting
state, or higher than 90 cycles per minute to exertion or state of emotion. The AP
waveform, the “slow action potential” (slow AP), is as shown in Fig. 4.2, left. The
electric wave generated by the SA node is transmitted through electrotonic conduc-
tion in the entire RA area and then through the interatrial beam to the left atrium
contractile volumes. Depolarization of the entire atrial area occurs in about 90 ms, at
B1 m/s (Morega, 1999).
SA discharge makes the electrical signal pass through the atria pathways, AV node, Hiss
bundle and the Purkinje network. This process triggers the normal heartbeat, the pulse.
The radial SA node depolarization takes approximately 100 ms and heads to the AV node,
which, due to low electrical conductivity, it traverses slower (0.02 0.05 m/s in B75 ms)
than the conductive tissue of the trunk and branches of Hiss (1 1.5 m/s), introducing a
100 ms delay (AV nodal delay) in the ventricles excitation. This time delay is controlled
through the sympathetic nerves, the “shortening” effect, and the vagi stimulation, the
“lengthening” effect. The wave travels in the heart from the base to the apex and from the
endocardium to the epicardium. The Purkinje network, characterized by the best electrical
conductivity values found in the entire electrical conduction system of the heart, rapidly
spreads out the depolarization wave further to the ventricles in 80 100 ms.
The impulses generated by conductive tissues are of lower amplitude and fre-
quency than that of the SA node. While not important in the functioning of the
healthy heart, they may take over the function of local tact generator when the heart
conduction pathway is disturbed (SA block, interatrial block, AV block, intraventricu-
lar block). This process affects the rhythmicity of the heart by desynchronizing the
atrial contractions from the ventricular ones. Thus the AV node generates depolariza-
tion pulses with a frequency of 40 60 cycles per minute, while the Purkinje
network produces pulses at the rate of 25 40 cycles per minute.