Page 208 - Computational Modeling in Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics
P. 208
Magnetic drug targeting 197
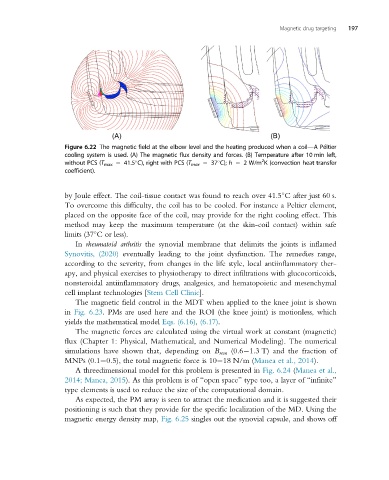
Figure 6.22 The magnetic field at the elbow level and the heating produced when a coil—APéltier
cooling system is used. (A) The magnetic flux density and forces. (B) Temperature after 10 min left,
2
without PCS (T max 5 41.5 C), right with PCS (T max 5 37 C); h 5 2W/m K (convection heat transfer
coefficient).
by Joule effect. The coil-tissue contact was found to reach over 41.5 C after just 60 s.
To overcome this difficulty, the coil has to be cooled. For instance a Peltier element,
placed on the opposite face of the coil, may provide for the right cooling effect. This
method may keep the maximum temperature (at the skin-coil contact) within safe
limits (37 C or less).
In rheumatoid arthritis the synovial membrane that delimits the joints is inflamed
Synovitis, (2020) eventually leading to the joint dysfunction. The remedies range,
according to the severity, from changes in the life style, local antiinflammatory ther-
apy, and physical exercises to physiotherapy to direct infiltrations with glucocorticoids,
nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, analgesics, and hematopoietic and mesenchymal
cell implant technologies [Stem Cell Clinic].
The magnetic field control in the MDT when applied to the knee joint is shown
in Fig. 6.23. PMs are used here and the ROI (the knee joint) is motionless, which
yields the mathematical model Eqs. (6.16), (6.17).
The magnetic forces are calculated using the virtual work at constant (magnetic)
flux (Chapter 1: Physical, Mathematical, and Numerical Modeling). The numerical
simulations have shown that, depending on B rem (0.6 1.3 T) and the fraction of
MNPs (0.1 0.5), the total magnetic force is 10 18 N/m (Manea et al., 2014).
A threedimensional model for this problem is presented in Fig. 6.24 (Manea et al.,
2014; Manea, 2015). As this problem is of “open space” type too, a layer of “infinite”
type elements is used to reduce the size of the computational domain.
As expected, the PM array is seen to attract the medication and it is suggested their
positioning is such that they provide for the specific localization of the MD. Using the
magnetic energy density map, Fig. 6.25 singles out the synovial capsule, and shows off