Page 60 - Computational Retinal Image Analysis
P. 60
50 CHAPTER 3 The physics, instruments and modalities of retinal imaging
Visible Optical Coherence Tomography (V-OCT). V-OCT is an emerging imag-
ing modality [61], providing novel capabilities of the current OCT instruments in
both anatomical and functional imaging of the eye. In contrast with most commer-
cial and research OCT devices, where near-infrared light is used for illumination,
it relies on visible light. Although V-OCT requires distinctive considerations in
devising the instrument and is mainly suitable for imaging superficial tissue due
to the limited depth penetration of visible light in tissue, it provides a much better
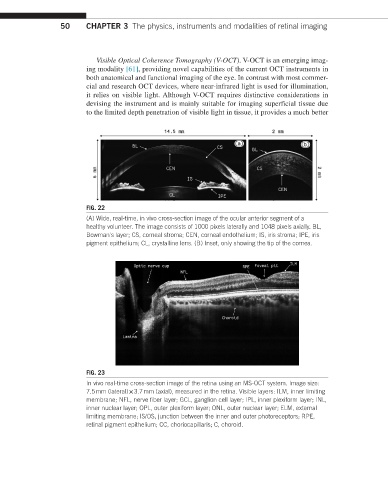
FIG. 22
(A) Wide, real-time, in vivo cross-section image of the ocular anterior segment of a
healthy volunteer. The image consists of 1000 pixels laterally and 1048 pixels axially. BL,
Bowman's layer; CS, corneal stroma; CEN, corneal endothelium; IS, iris stroma; IPE, iris
pigment epithelium; CL, crystalline lens. (B) Inset, only showing the tip of the cornea.
FIG. 23
In vivo real-time cross-section image of the retina using an MS-OCT system. Image size:
7.5 mm (lateral) × 3.7 mm (axial), measured in the retina. Visible layers: ILM, inner limiting
membrane; NFL, nerve fiber layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL,
inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; ELM, external
limiting membrane; IS/OS, junction between the inner and outer photoreceptors; RPE,
retinal pigment epithelium; CC, choriocapillaris; C, choroid.