Page 367 - Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
P. 367
356 Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
Subtree − T
5
x1 < 0.031
x2 < 0.58
C− 1
x1 < 0.5
C− 2
C− 2 C− 1
GU
IG
F F FI F II U URE G 9.1 RE RE RE 9.1 4 4 4 4
9.1
9.1
GU
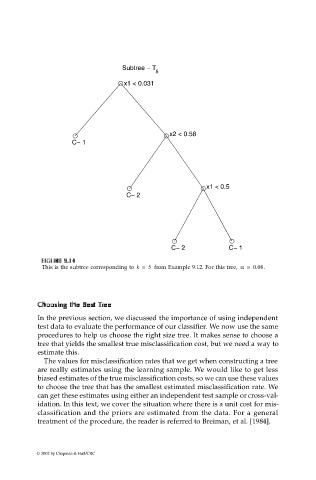
This is the subtree corresponding to k = 5 from Example 9.12. For this tree, α = 0.08.
ee
e
gg
th
thth
BeBe
ChoosinChoosin
Choosin h e eB Be s st sstt tT TTrr eeee
Choosin
Tr
reeee
g
gt
In the previous section, we discussed the importance of using independent
test data to evaluate the performance of our classifier. We now use the same
procedures to help us choose the right size tree. It makes sense to choose a
tree that yields the smallest true misclassification cost, but we need a way to
estimate this.
The values for misclassification rates that we get when constructing a tree
are really estimates using the learning sample. We would like to get less
biased estimates of the true misclassification costs, so we can use these values
to choose the tree that has the smallest estimated misclassification rate. We
can get these estimates using either an independent test sample or cross-val-
idation. In this text, we cover the situation where there is a unit cost for mis-
classification and the priors are estimated from the data. For a general
treatment of the procedure, the reader is referred to Breiman, et al. [1984].
© 2002 by Chapman & Hall/CRC