Page 259 -
P. 259
226 CHAPTER 7 / INPUT/OUTPUT
Issue read Issue read CPU I/O Issue read CPU DMA
command to CPU I/O command to Do something block command Do something
I/O module I/O module else to I/O module else
Read status Read status Interrupt Read status Interrupt
of I/O I/O CPU of I/O of DMA
module module I/O CPU module DMA CPU
Not
ready Next instruction
Check Error Check Error
Status Condition status condition (c) Direct Memory Access
Ready Ready
Read word Read word
from I/O I/O CPU from I/O I/O CPU
module module
Write word Write word
into memory CPU Memory into memory CPU Memory
No No
Done? Done?
Yes Yes
Next instruction Next instruction
(a) Programmed I/O (b) Interrupt-Driven I/O
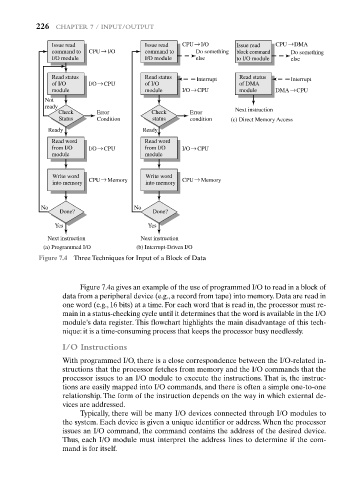
Figure 7.4 Three Techniques for Input of a Block of Data
Figure 7.4a gives an example of the use of programmed I/O to read in a block of
data from a peripheral device (e.g., a record from tape) into memory. Data are read in
one word (e.g., 16 bits) at a time. For each word that is read in, the processor must re-
main in a status-checking cycle until it determines that the word is available in the I/O
module’s data register. This flowchart highlights the main disadvantage of this tech-
nique: it is a time-consuming process that keeps the processor busy needlessly.
I/O Instructions
With programmed I/O, there is a close correspondence between the I/O-related in-
structions that the processor fetches from memory and the I/O commands that the
processor issues to an I/O module to execute the instructions. That is, the instruc-
tions are easily mapped into I/O commands, and there is often a simple one-to-one
relationship. The form of the instruction depends on the way in which external de-
vices are addressed.
Typically, there will be many I/O devices connected through I/O modules to
the system. Each device is given a unique identifier or address. When the processor
issues an I/O command, the command contains the address of the desired device.
Thus, each I/O module must interpret the address lines to determine if the com-
mand is for itself.