Page 57 -
P. 57
2.1 / A BRIEF HISTORY OF COMPUTERS 33
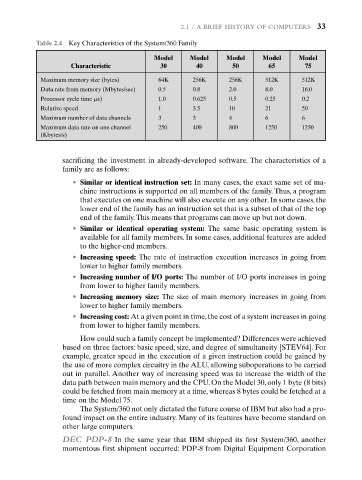
Table 2.4 Key Characteristics of the System/360 Family
Model Model Model Model Model
Characteristic 30 40 50 65 75
Maximum memory size (bytes) 64K 256K 256K 512K 512K
Data rate from memory (Mbytes/sec) 0.5 0.8 2.0 8.0 16.0
Processor cycle time s)m 1.0 0.625 0.5 0.25 0.2
Relative speed 1 3.5 10 21 50
Maximum number of data channels 3 3 4 6 6
Maximum data rate on one channel 250 400 800 1250 1250
(Kbytes/s)
sacrificing the investment in already-developed software. The characteristics of a
family are as follows:
• Similar or identical instruction set: In many cases, the exact same set of ma-
chine instructions is supported on all members of the family. Thus, a program
that executes on one machine will also execute on any other. In some cases, the
lower end of the family has an instruction set that is a subset of that of the top
end of the family.This means that programs can move up but not down.
• Similar or identical operating system: The same basic operating system is
available for all family members. In some cases, additional features are added
to the higher-end members.
• Increasing speed: The rate of instruction execution increases in going from
lower to higher family members.
• Increasing number of I/O ports: The number of I/O ports increases in going
from lower to higher family members.
• Increasing memory size: The size of main memory increases in going from
lower to higher family members.
• Increasing cost: At a given point in time, the cost of a system increases in going
from lower to higher family members.
How could such a family concept be implemented? Differences were achieved
based on three factors: basic speed, size, and degree of simultaneity [STEV64]. For
example, greater speed in the execution of a given instruction could be gained by
the use of more complex circuitry in the ALU, allowing suboperations to be carried
out in parallel. Another way of increasing speed was to increase the width of the
data path between main memory and the CPU. On the Model 30, only 1 byte (8 bits)
could be fetched from main memory at a time, whereas 8 bytes could be fetched at a
time on the Model 75.
The System/360 not only dictated the future course of IBM but also had a pro-
found impact on the entire industry. Many of its features have become standard on
other large computers.
DEC PDP-8 In the same year that IBM shipped its first System/360, another
momentous first shipment occurred: PDP-8 from Digital Equipment Corporation