Page 62 -
P. 62
2.1 / A BRIEF HISTORY OF COMPUTERS 37
This evolution can be seen most easily in the number of bits that the processor
deals with at a time.There is no clear-cut measure of this, but perhaps the best mea-
sure is the data bus width: the number of bits of data that can be brought into or sent
out of the processor at a time. Another measure is the number of bits in the accu-
mulator or in the set of general-purpose registers. Often, these measures coincide,
but not always. For example, a number of microprocessors were developed that op-
erate on 16-bit numbers in registers but can only read and write 8 bits at a time.
The next major step in the evolution of the microprocessor was the introduc-
tion in 1972 of the Intel 8008.This was the first 8-bit microprocessor and was almost
twice as complex as the 4004.
Neither of these steps was to have the impact of the next major event: the in-
troduction in 1974 of the Intel 8080.This was the first general-purpose microproces-
sor. Whereas the 4004 and the 8008 had been designed for specific applications, the
8080 was designed to be the CPU of a general-purpose microcomputer. Like the
8008, the 8080 is an 8-bit microprocessor. The 8080, however, is faster, has a richer
instruction set, and has a large addressing capability.
About the same time, 16-bit microprocessors began to be developed. How-
ever, it was not until the end of the 1970s that powerful, general-purpose 16-bit mi-
croprocessors appeared. One of these was the 8086. The next step in this trend
occurred in 1981, when both Bell Labs and Hewlett-Packard developed 32-bit, sin-
gle-chip microprocessors. Intel introduced its own 32-bit microprocessor, the 80386,
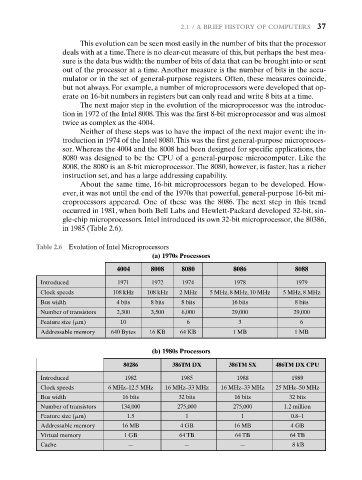
in 1985 (Table 2.6).
Table 2.6 Evolution of Intel Microprocessors
(a) 1970s Processors
4004 8008 8080 8086 8088
Introduced 1971 1972 1974 1978 1979
Clock speeds 108 kHz 108 kHz 2 MHz 5 MHz, 8 MHz, 10 MHz 5 MHz, 8 MHz
Bus width 4 bits 8 bits 8 bits 16 bits 8 bits
Number of transistors 2,300 3,500 6,000 29,000 29,000
Feature size ( m)m 10 6 3 6
Addressable memory 640 Bytes 16 KB 64 KB 1 MB 1 MB
(b) 1980s Processors
80286 386TM DX 386TM SX 486TM DX CPU
Introduced 1982 1985 1988 1989
Clock speeds 6 MHz–12.5 MHz 16 MHz–33 MHz 16 MHz–33 MHz 25 MHz–50 MHz
Bus width 16 bits 32 bits 16 bits 32 bits
Number of transistors 134,000 275,000 275,000 1.2 million
Feature size ( m)m 1.5 1 1 0.8–1
Addressable memory 16 MB 4 GB 16 MB 4 GB
Virtual memory 1 GB 64 TB 64 TB 64 TB
Cache — — — 8 kB