Page 68 -
P. 68
2.2 / DESIGNING FOR PERFORMANCE 43
Hyperthreading
(multicore)
10,000
Longer pipeline,
double-speed
Improvements in
chip architecture arithmetic
Increases in Full-speed
clock speed 2-level cache
1,000 Speculative extensions
Theoretical maximum performance (million operations per second) 100 instructions out-of-order 733 MHz 2000 MHz
MMX
multimedia
3060 MHz
execution
Multiple
per cycle
Internal
cache
Instruction memory 200 MHz 300 MHz
pipeline
10
66 MHz
50 MHz
33 MHz
25 MHz
16 MHz
1
1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004
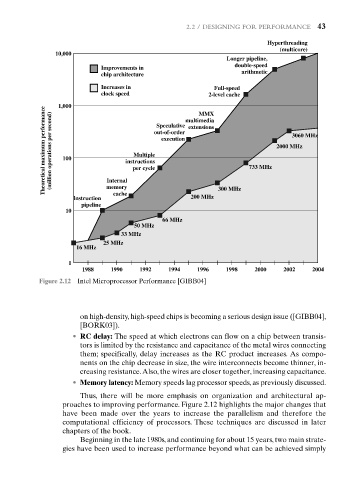
Figure 2.12 Intel Microprocessor Performance [GIBB04]
on high-density, high-speed chips is becoming a serious design issue ([GIBB04],
[BORK03]).
• RC delay: The speed at which electrons can flow on a chip between transis-
tors is limited by the resistance and capacitance of the metal wires connecting
them; specifically, delay increases as the RC product increases. As compo-
nents on the chip decrease in size, the wire interconnects become thinner, in-
creasing resistance.Also, the wires are closer together, increasing capacitance.
• Memory latency: Memory speeds lag processor speeds, as previously discussed.
Thus, there will be more emphasis on organization and architectural ap-
proaches to improving performance. Figure 2.12 highlights the major changes that
have been made over the years to increase the parallelism and therefore the
computational efficiency of processors. These techniques are discussed in later
chapters of the book.
Beginning in the late 1980s, and continuing for about 15 years, two main strate-
gies have been used to increase performance beyond what can be achieved simply