Page 92 -
P. 92
3.1 / COMPUTER COMPONENTS 67
• Data and instructions are stored in a single read–write memory.
• The contents of this memory are addressable by location, without regard to
the type of data contained there.
• Execution occurs in a sequential fashion (unless explicitly modified) from one
instruction to the next.
The reasoning behind these concepts was discussed in Chapter 2 but is worth
summarizing here. There is a small set of basic logic components that can be com-
bined in various ways to store binary data and to perform arithmetic and logical op-
erations on that data. If there is a particular computation to be performed, a
configuration of logic components designed specifically for that computation could
be constructed.We can think of the process of connecting the various components in
the desired configuration as a form of programming. The resulting “program” is in
the form of hardware and is termed a hardwired program.
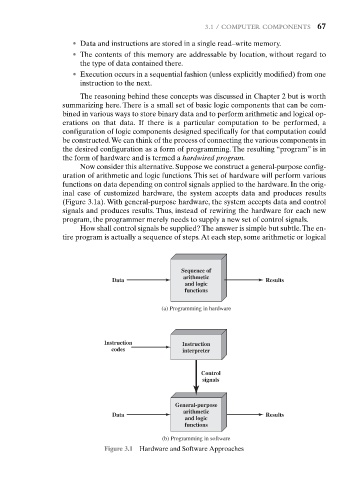
Now consider this alternative. Suppose we construct a general-purpose config-
uration of arithmetic and logic functions. This set of hardware will perform various
functions on data depending on control signals applied to the hardware. In the orig-
inal case of customized hardware, the system accepts data and produces results
(Figure 3.1a). With general-purpose hardware, the system accepts data and control
signals and produces results. Thus, instead of rewiring the hardware for each new
program, the programmer merely needs to supply a new set of control signals.
How shall control signals be supplied? The answer is simple but subtle.The en-
tire program is actually a sequence of steps.At each step, some arithmetic or logical
Sequence of
arithmetic
Data Results
and logic
functions
(a) Programming in hardware
Instruction Instruction
codes interpreter
Control
signals
General-purpose
arithmetic
Data Results
and logic
functions
(b) Programming in software
Figure 3.1 Hardware and Software Approaches