Page 94 -
P. 94
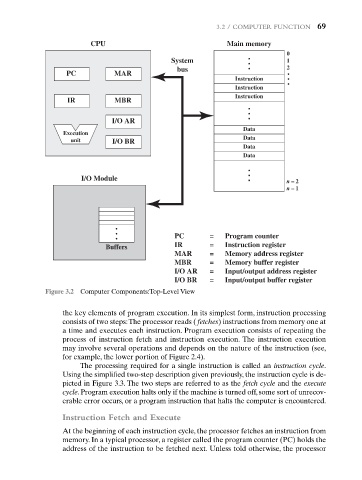
3.2 / COMPUTER FUNCTION 69
CPU Main memory
0
System 1
bus 2
PC MAR
Instruction
Instruction
Instruction
IR MBR
I/O AR
Data
Execution
unit I/O BR Data
Data
Data
I/O Module n – 2
n – 1
PC = Program counter
Buffers IR = Instruction register
MAR = Memory address register
MBR = Memory buffer register
I/O AR = Input/output address register
I/O BR = Input/output buffer register
Figure 3.2 Computer Components:Top-Level View
the key elements of program execution. In its simplest form, instruction processing
consists of two steps:The processor reads ( fetches) instructions from memory one at
a time and executes each instruction. Program execution consists of repeating the
process of instruction fetch and instruction execution. The instruction execution
may involve several operations and depends on the nature of the instruction (see,
for example, the lower portion of Figure 2.4).
The processing required for a single instruction is called an instruction cycle.
Using the simplified two-step description given previously, the instruction cycle is de-
picted in Figure 3.3. The two steps are referred to as the fetch cycle and the execute
cycle. Program execution halts only if the machine is turned off, some sort of unrecov-
erable error occurs, or a program instruction that halts the computer is encountered.
Instruction Fetch and Execute
At the beginning of each instruction cycle, the processor fetches an instruction from
memory. In a typical processor, a register called the program counter (PC) holds the
address of the instruction to be fetched next. Unless told otherwise, the processor