Page 75 -
P. 75
54 2 Image formation
light
source
^
n
image plane
sensor
plane
surface
optics
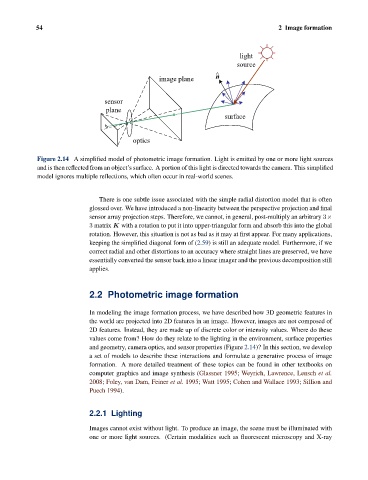
Figure 2.14 A simplified model of photometric image formation. Light is emitted by one or more light sources
and is then reflected from an object’s surface. A portion of this light is directed towards the camera. This simplified
model ignores multiple reflections, which often occur in real-world scenes.
There is one subtle issue associated with the simple radial distortion model that is often
glossed over. We have introduced a non-linearity between the perspective projection and final
sensor array projection steps. Therefore, we cannot, in general, post-multiply an arbitrary 3×
3 matrix K with a rotation to put it into upper-triangular form and absorb this into the global
rotation. However, this situation is not as bad as it may at first appear. For many applications,
keeping the simplified diagonal form of (2.59) is still an adequate model. Furthermore, if we
correct radial and other distortions to an accuracy where straight lines are preserved, we have
essentially converted the sensor back into a linear imager and the previous decomposition still
applies.
2.2 Photometric image formation
In modeling the image formation process, we have described how 3D geometric features in
the world are projected into 2D features in an image. However, images are not composed of
2D features. Instead, they are made up of discrete color or intensity values. Where do these
values come from? How do they relate to the lighting in the environment, surface properties
and geometry, camera optics, and sensor properties (Figure 2.14)? In this section, we develop
a set of models to describe these interactions and formulate a generative process of image
formation. A more detailed treatment of these topics can be found in other textbooks on
computer graphics and image synthesis (Glassner 1995; Weyrich, Lawrence, Lensch et al.
2008; Foley, van Dam, Feiner et al. 1995; Watt 1995; Cohen and Wallace 1993; Sillion and
Puech 1994).
2.2.1 Lighting
Images cannot exist without light. To produce an image, the scene must be illuminated with
one or more light sources. (Certain modalities such as fluorescent microscopy and X-ray