Page 35 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 35
are identical, except that they are mirror images with respect to the x axis.
All the divisions represent the same unit distance in either case. While
left and right are reversed in this example, the senses of up/down and
forward/backward remain the same.
In some systems, it is necessary to invert two, or even all three, axes to
obtain the desired robot motion. These schemes can be called dual-axis
inversion or triple-axis inversion.
See also AXIS INTERCHANGE and CARTESIAN COORDINATE GEOMETRY.
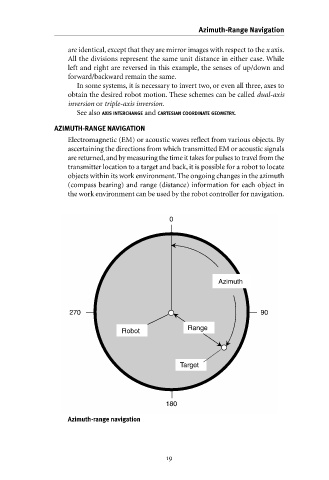
AZIMUTH-RANGE NAVIGATION Azimuth-Range Navigation
Electromagnetic (EM) or acoustic waves reflect from various objects. By
ascertaining the directions from which transmitted EM or acoustic signals
are returned,and by measuring the time it takes for pulses to travel from the
transmitter location to a target and back, it is possible for a robot to locate
objects within its work environment. The ongoing changes in the azimuth
(compass bearing) and range (distance) information for each object in
the work environment can be used by the robot controller for navigation.
0
Azimuth
270 90
Range
Robot
Target
180
Azimuth-range navigation