Page 39 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 39
Bandwidth
The main assets of ballistic control are simplicity and moderate cost.
A robotic manipulator with ballistic control does not have to carry sensors;
a mobile robot with ballistic control does not need its own on-board
computer. The main limitation is the fact that ballistic control does not
allow for rapid,localized,or unexpected changes in the work environment.
Compare CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL.
BANDWIDTH
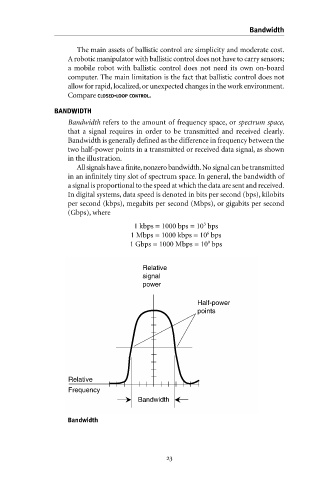
Bandwidth refers to the amount of frequency space, or spectrum space,
that a signal requires in order to be transmitted and received clearly.
Bandwidth is generally defined as the difference in frequency between the
two half-power points in a transmitted or received data signal, as shown
in the illustration.
All signals have a finite,nonzero bandwidth.No signal can be transmitted
in an infinitely tiny slot of spectrum space. In general, the bandwidth of
a signal is proportional to the speed at which the data are sent and received.
In digital systems, data speed is denoted in bits per second (bps), kilobits
per second (kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second
(Gbps), where
3
1 kbps = 1000 bps = 10 bps
6
1 Mbps = 1000 kbps = 10 bps
9
1 Gbps = 1000 Mbps = 10 bps
Relative
signal
power
Half-power
points
Relative
Frequency
Bandwidth
Bandwidth