Page 42 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 42
Binary Number System
Shoreline
sighted Shoreline Dock
Boat follows
shoreline
Initial course
Initial position
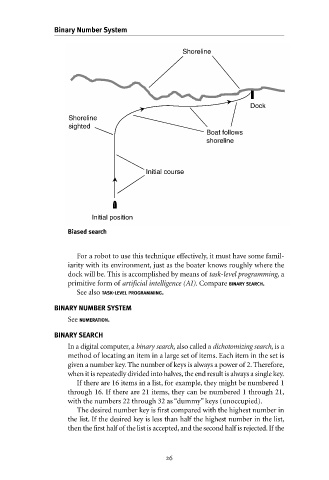
Biased search
For a robot to use this technique effectively, it must have some famil-
iarity with its environment, just as the boater knows roughly where the
dock will be. This is accomplished by means of task-level programming, a
primitive form of artificial intelligence (AI). Compare BINARY SEARCH.
See also TASK-LEVEL PROGRAMMING.
BINARY NUMBER SYSTEM
See NUMERATION.
BINARY SEARCH
In a digital computer, a binary search, also called a dichotomizing search, is a
method of locating an item in a large set of items. Each item in the set is
given a number key. The number of keys is always a power of 2. Therefore,
when it is repeatedly divided into halves,the end result is always a single key.
If there are 16 items in a list, for example, they might be numbered 1
through 16. If there are 21 items, they can be numbered 1 through 21,
with the numbers 22 through 32 as “dummy” keys (unoccupied).
The desired number key is first compared with the highest number in
the list. If the desired key is less than half the highest number in the list,
then the first half of the list is accepted,and the second half is rejected.If the