Page 38 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 38
Backward Chaining
Torque
Robot
arm
Back
Motor
pressure
Sensor Force Load
Resistance
Signal
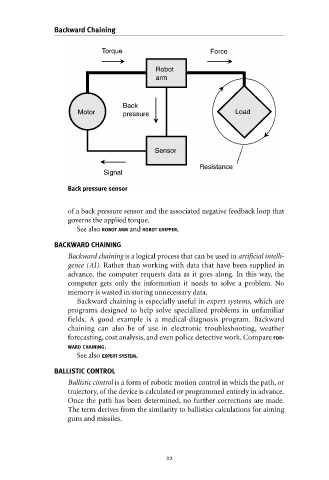
Back pressure sensor
of a back pressure sensor and the associated negative feedback loop that
governs the applied torque.
See also ROBOT ARM and ROBOT GRIPPER.
BACKWARD CHAINING
Backward chaining is a logical process that can be used in artificial intelli-
gence (AI). Rather than working with data that have been supplied in
advance, the computer requests data as it goes along. In this way, the
computer gets only the information it needs to solve a problem. No
memory is wasted in storing unnecessary data.
Backward chaining is especially useful in expert systems, which are
programs designed to help solve specialized problems in unfamiliar
fields. A good example is a medical-diagnosis program. Backward
chaining can also be of use in electronic troubleshooting, weather
forecasting, cost analysis, and even police detective work. Compare FOR-
WARD CHAINING.
See also EXPERT SYSTEM.
BALLISTIC CONTROL
Ballistic control is a form of robotic motion control in which the path, or
trajectory, of the device is calculated or programmed entirely in advance.
Once the path has been determined, no further corrections are made.
The term derives from the similarity to ballistics calculations for aiming
guns and missiles.