Page 57 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 57
Cartesian Coordinate Geometry
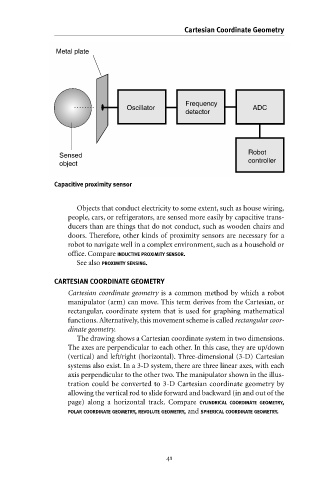
Metal plate
Frequency
ADC
Oscillator
detector
Robot
Sensed
object controller
Capacitive proximity sensor
Objects that conduct electricity to some extent, such as house wiring,
people, cars, or refrigerators, are sensed more easily by capacitive trans-
ducers than are things that do not conduct, such as wooden chairs and
doors. Therefore, other kinds of proximity sensors are necessary for a
robot to navigate well in a complex environment, such as a household or
office. Compare INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR.
See also PROXIMITY SENSING.
CARTESIAN COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Cartesian coordinate geometry is a common method by which a robot
manipulator (arm) can move. This term derives from the Cartesian, or
rectangular, coordinate system that is used for graphing mathematical
functions.Alternatively, this movement scheme is called rectangular coor-
dinate geometry.
The drawing shows a Cartesian coordinate system in two dimensions.
The axes are perpendicular to each other. In this case, they are up/down
(vertical) and left/right (horizontal). Three-dimensional (3-D) Cartesian
systems also exist. In a 3-D system, there are three linear axes, with each
axis perpendicular to the other two. The manipulator shown in the illus-
tration could be converted to 3-D Cartesian coordinate geometry by
allowing the vertical rod to slide forward and backward (in and out of the
page) along a horizontal track. Compare CYLINDRICAL COORDINATE GEOMETRY,
POLAR COORDINATE GEOMETRY, REVOLUTE GEOMETRY, and SPHERICAL COORDINATE GEOMETRY.