Page 62 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 62
Clinometer
The contamination in a clean room is measured in terms of the number
of particles of a certain size in 1 liter (1000 cubic centimeters) of air. Alter-
natively, the cubic foot is used as the standard unit of volume.
See also INTEGRATED CIRCUIT.
CLINOMETER
A clinometer is a device for measuring the steepness of a sloping surface.
Mobile robots use clinometers to avoid inclines that might cause them to
tip too far, possibly even falling over.
The floor in a building is almost always horizontal. Thus, its incline
is zero. But sometimes there are inclines such as ramps.A good example is
the kind of ramp used for wheelchairs, in which a very small elevation
change occurs. A rolling robot cannot climb stairs, but it might use a
wheelchair ramp, provided the ramp is not so steep that it upsets the
robot’s balance or causes it to spill or drop its payload.
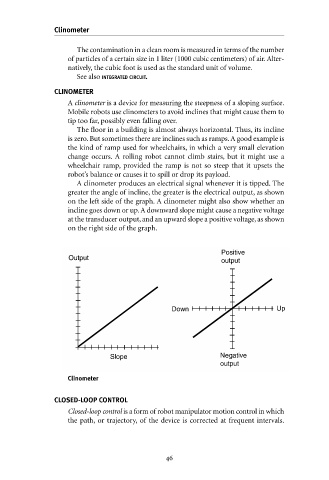
A clinometer produces an electrical signal whenever it is tipped. The
greater the angle of incline, the greater is the electrical output, as shown
on the left side of the graph. A clinometer might also show whether an
incline goes down or up.A downward slope might cause a negative voltage
at the transducer output, and an upward slope a positive voltage, as shown
on the right side of the graph.
Positive
Output output
Down Up
Slope Negative
output
Clinometer
CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL
Closed-loop control is a form of robot manipulator motion control in which
the path, or trajectory, of the device is corrected at frequent intervals.