Page 79 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 79
66 Control theory in biomedical engineering
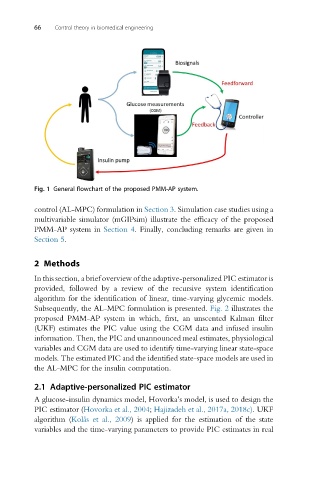
Fig. 1 General flowchart of the proposed PMM-AP system.
control (AL-MPC) formulation in Section 3. Simulation case studies using a
multivariable simulator (mGIPsim) illustrate the efficacy of the proposed
PMM-AP system in Section 4. Finally, concluding remarks are given in
Section 5.
2Methods
In this section, a brief overview of the adaptive-personalized PIC estimator is
provided, followed by a review of the recursive system identification
algorithm for the identification of linear, time-varying glycemic models.
Subsequently, the AL-MPC formulation is presented. Fig. 2 illustrates the
proposed PMM-AP system in which, first, an unscented Kalman filter
(UKF) estimates the PIC value using the CGM data and infused insulin
information. Then, the PIC and unannounced meal estimates, physiological
variables and CGM data are used to identify time-varying linear state-space
models. The estimated PIC and the identified state-space models are used in
the AL-MPC for the insulin computation.
2.1 Adaptive-personalized PIC estimator
A glucose-insulin dynamics model, Hovorka’s model, is used to design the
PIC estimator (Hovorka et al., 2004; Hajizadeh et al., 2017a, 2018c). UKF
algorithm (Kola ˚s et al., 2009) is applied for the estimation of the state
variables and the time-varying parameters to provide PIC estimates in real