Page 326 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 326
296 C h a p t e r 8 C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 297
220 kV to transmission power
11.5 kV 35-MW steam
generation turbine generator Air discharge
voltage
HP turbine
LP turbine Water spray
Generator
gearbox Cooling air Cooling air
220/11.5 kV
Transformer LP steam
Cooling tower
to chillers
1.55 Bar
High pressure steam LP steam to host
92 Bar(g) Stack 9.1 Bar
Deaerator
Once-
No control steam through
X
HRSG
Hot well
Natural gas
Air intake LP feed
pump
HP feed
pump
City
2 × 44 MW Duct burner Treated Raw water
Gas turbine generators water tank water tank
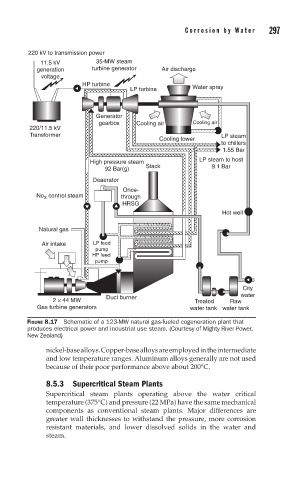
FIGURE 8.17 Schematic of a 123-MW natural gas-fueled cogeneration plant that
produces electrical power and industrial use steam. (Courtesy of Mighty River Power,
New Zealand)
nickel-base alloys. Copper-base alloys are employed in the intermediate
and low temperature ranges. Aluminum alloys generally are not used
because of their poor performance above about 200°C.
8.5.3 Supercritical Steam Plants
Supercritical steam plants operating above the water critical
temperature (375°C) and pressure (22 MPa) have the same mechanical
components as conventional steam plants. Major differences are
greater wall thicknesses to withstand the pressure, more corrosion
resistant materials, and lower dissolved solids in the water and
steam.