Page 339 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 339
310 C h a p t e r 8 C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 311
Commercial formulations generally consist of one or more inhibitor
compounds with other additives such as surfactants, film enhancers,
de-emulsifiers, oxygen scavengers, and so forth. The inhibitor solvent
package used can be critical in respect to the solubility/dispersibility
characteristics and hence the application and performance of the
products.
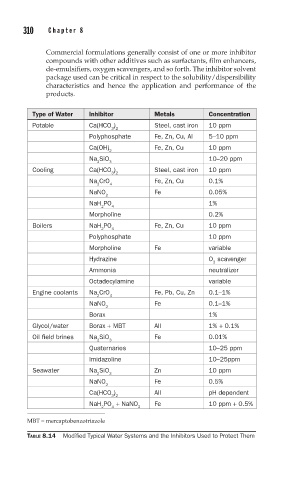
Type of Water Inhibitor Metals Concentration
Potable Ca(HCO ) Steel, cast iron 10 ppm
3 2
Polyphosphate Fe, Zn, Cu, Al 5–10 ppm
Ca(OH) Fe, Zn, Cu 10 ppm
2
Na SiO 10–20 ppm
2 3
Cooling Ca(HCO ) Steel, cast iron 10 ppm
3 2
Na CrO Fe, Zn, Cu 0.1%
2 4
NaNO Fe 0.05%
2
NaH PO 1%
2 4
Morpholine 0.2%
Boilers NaH PO Fe, Zn, Cu 10 ppm
2 4
Polyphosphate 10 ppm
Morpholine Fe variable
Hydrazine O scavenger
2
Ammonia neutralizer
Octadecylamine variable
Engine coolants Na CrO Fe, Pb, Cu, Zn 0.1–1%
2 4
NaNO Fe 0.1–1%
2
Borax 1%
Glycol/water Borax + MBT All 1% + 0.1%
Oil field brines Na SiO Fe 0.01%
2 3
Quaternaries 10–25 ppm
Imidazoline 10–25ppm
Seawater Na SiO Zn 10 ppm
2 3
NaNO Fe 0.5%
2
Ca(HCO ) All pH dependent
3 2
NaH PO + NaNO Fe 10 ppm + 0.5%
2 4 2
MBT = mercaptobenzotriazole
TABLE 8.14 Modified Typical Water Systems and the Inhibitors Used to Protect Them