Page 337 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 337
308 C h a p t e r 8 C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 309
water, more treatment is required. As for any water source that is not
properly treated, health problems could arise from drinking or being
exposed to recycled water if it contains disease-causing organisms or
other contaminants.
There is no single valid solution with regard to water treatments.
The specific conditions of water supplies can be vastly different, even
in systems separated by only a few meters. The evaluation of the
water quality is typically determined by a chemical water analysis [9].
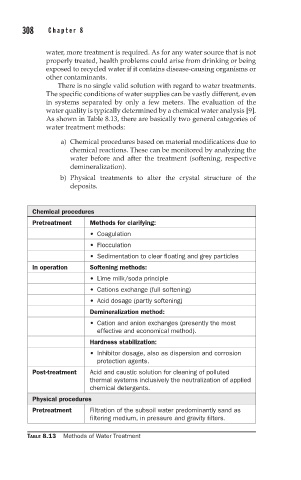
As shown in Table 8.13, there are basically two general categories of
water treatment methods:
a) Chemical procedures based on material modifications due to
chemical reactions. These can be monitored by analyzing the
water before and after the treatment (softening, respective
demineralization).
b) Physical treatments to alter the crystal structure of the
deposits.
Chemical procedures
Pretreatment Methods for clarifying:
• Coagulation
• Flocculation
• Sedimentation to clear floating and grey particles
In operation Softening methods:
• Lime milk/soda principle
• Cations exchange (full softening)
• Acid dosage (partly softening)
Demineralization method:
• Cation and anion exchanges (presently the most
effective and economical method).
Hardness stabilization:
• Inhibitor dosage, also as dispersion and corrosion
protection agents.
Post-treatment Acid and caustic solution for cleaning of polluted
thermal systems inclusively the neutralization of applied
chemical detergents.
Physical procedures
Pretreatment Filtration of the subsoil water predominantly sand as
filtering medium, in pressure and gravity filters.
TABLE 8.13 Methods of Water Treatment