Page 335 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 335
306 C h a p t e r 8 C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 307
Two factors that are not monitored often enough in the power
producing industry are thermal stresses in heavy sections, which can
lead to low-cycle corrosion fatigue (CF), and vibration in rotating
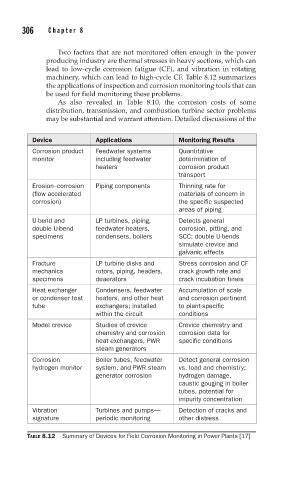
machinery, which can lead to high-cycle CF. Table 8.12 summarizes
the applications of inspection and corrosion monitoring tools that can
be used for field monitoring these problems.
As also revealed in Table 8.10, the corrosion costs of some
distribution, transmission, and combustion turbine sector problems
may be substantial and warrant attention. Detailed discussions of the
Device Applications Monitoring Results
Corrosion product Feedwater systems Quantitative
monitor including feedwater determination of
heaters corrosion product
transport
Erosion–corrosion Piping components Thinning rate for
(flow accelerated materials of concern in
corrosion) the specific suspected
areas of piping
U-bend and LP turbines, piping, Detects general
double U-bend feedwater heaters, corrosion, pitting, and
specimens condensers, boilers SCC; double U-bends
simulate crevice and
galvanic effects
Fracture LP turbine disks and Stress corrosion and CF
mechanics rotors, piping, headers, crack growth rate and
specimens deaerators crack incubation times
Heat exchanger Condensers, feedwater Accumulation of scale
or condenser test heaters, and other heat and corrosion pertinent
tube exchangers; installed to plant-specific
within the circuit conditions
Model crevice Studies of crevice Crevice chemistry and
chemistry and corrosion corrosion data for
heat exchangers, PWR specific conditions
steam generators
Corrosion Boiler tubes, feedwater Detect general corrosion
hydrogen monitor system, and PWR steam vs. load and chemistry;
generator corrosion hydrogen damage,
caustic gouging in boiler
tubes, potential for
impurity concentration
Vibration Turbines and pumps— Detection of cracks and
signature periodic monitoring other distress
TABLE 8.12 Summary of Devices for Field Corrosion Monitoring in Power Plants [17]