Page 333 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 333
304 C h a p t e r 8
The total cost of the listed items is approximately $11.7 billion or
76 percent of the total $15.4 billion cost of corrosion for 1998. The
balance of the corrosion cost ($3.7 billion) likely stems from many
miscellaneous less costly corrosion problems. As shown in Table 8.10,
corrosion costs in the nuclear power and fossil steam power sectors
dominate corrosion costs in the electric power industry. The very
large cost problems in the nuclear and fossil sectors at the top of the
list warrant serious attention.
Some special monitoring techniques are available to supplement
normal water chemistry control in these important industrial applications.
These tools are designed to help operators carry out specific monitoring
tasks, for example, scale and deposits, composition of moisture droplets
and liquid film in two-phase regions, in situ corrosion potential, at-
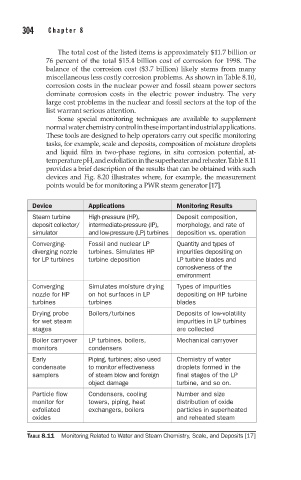
temperature pH, and exfoliation in the superheater and reheater. Table 8.11
provides a brief description of the results that can be obtained with such
devices and Fig. 8.20 illustrates where, for example, the measurement
points would be for monitoring a PWR steam generator [17].
Device Applications Monitoring Results
Steam turbine High-pressure (HP), Deposit composition,
deposit collector/ intermediate-pressure (IP), morphology, and rate of
simulator and low-pressure (LP) turbines deposition vs. operation
Converging- Fossil and nuclear LP Quantity and types of
diverging nozzle turbines. Simulates HP impurities depositing on
for LP turbines turbine deposition LP turbine blades and
corrosiveness of the
environment
Converging Simulates moisture drying Types of impurities
nozzle for HP on hot surfaces in LP depositing on HP turbine
turbines turbines blades
Drying probe Boilers/turbines Deposits of low-volatility
for wet steam impurities in LP turbines
stages are collected
Boiler carryover LP turbines, boilers, Mechanical carryover
monitors condensers
Early Piping, turbines; also used Chemistry of water
condensate to monitor effectiveness droplets formed in the
samplers of steam blow and foreign final stages of the LP
object damage turbine, and so on.
Particle flow Condensers, cooling Number and size
monitor for towers, piping, heat distribution of oxide
exfoliated exchangers, boilers particles in superheated
oxides and reheated steam
TABLE 8.11 Monitoring Related to Water and Steam Chemistry, Scale, and Deposits [17]
305