Page 411 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 411
380 C h a p t e r 9 A t m o s p h e r i c C o r r o s i o n 381
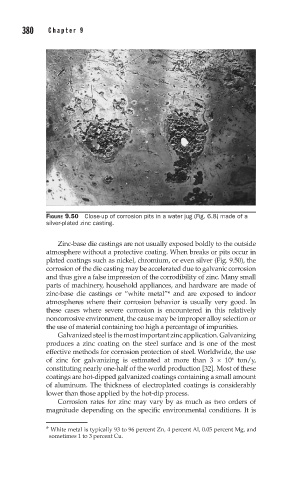
FIGURE 9.50 Close-up of corrosion pits in a water jug (Fig. 6.8) made of a
silver-plated zinc casting.
Zinc-base die castings are not usually exposed boldly to the outside
atmosphere without a protective coating. When breaks or pits occur in
plated coatings such as nickel, chromium, or even silver (Fig. 9.50), the
corrosion of the die casting may be accelerated due to galvanic corrosion
and thus give a false impression of the corrodibility of zinc. Many small
parts of machinery, household appliances, and hardware are made of
zinc-base die castings or “white metal”* and are exposed to indoor
atmospheres where their corrosion behavior is usually very good. In
these cases where severe corrosion is encountered in this relatively
noncorrosive environment, the cause may be improper alloy selection or
the use of material containing too high a percentage of impurities.
Galvanized steel is the most important zinc application. Galvanizing
produces a zinc coating on the steel surface and is one of the most
effective methods for corrosion protection of steel. Worldwide, the use
of zinc for galvanizing is estimated at more than 3 × 10 ton/y,
6
constituting nearly one-half of the world production [32]. Most of these
coatings are hot-dipped galvanized coatings containing a small amount
of aluminum. The thickness of electroplated coatings is considerably
lower than those applied by the hot-dip process.
Corrosion rates for zinc may vary by as much as two orders of
magnitude depending on the specific environmental conditions. It is
* White metal is typically 93 to 96 percent Zn, 4 percent Al, 0.05 percent Mg, and
sometimes 1 to 3 percent Cu.