Page 549 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 549
512 C h a p t e r 1 2 C o r r o s i o n a s a R i s k 513
spends approximately seven billion dollars per year on corrosion
control. This figure includes operations and maintenance activities,
capital expenditures, and corrosion failure repairs [18]. The tools most
commonly used by operators to verify pipeline integrity include both
external and internal direct assessments, hydrostatic testing, and in-
line inspection (ILI). Each of these tools can be used under various
circumstances for baseline assessments and future reassessments.
12.7.1 External Corrosion Damage Assessment
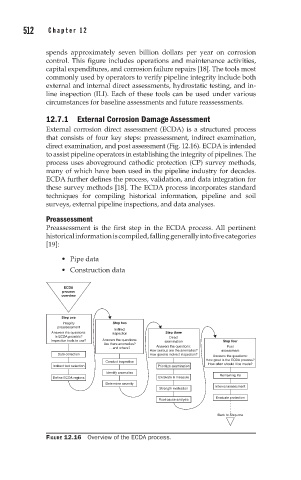
External corrosion direct assessment (ECDA) is a structured process
that consists of four key steps: preassessment, indirect examination,
direct examination, and post assessment (Fig. 12.16). ECDA is intended
to assist pipeline operators in establishing the integrity of pipelines. The
process uses aboveground cathodic protection (CP) survey methods,
many of which have been used in the pipeline industry for decades.
ECDA further defines the process, validation, and data integration for
these survey methods [18]. The ECDA process incorporates standard
techniques for compiling historical information, pipeline and soil
surveys, external pipeline inspections, and data analyses.
Preassessment
Preassessment is the first step in the ECDA process. All pertinent
historical information is compiled, falling generally into five categories
[19]:
• Pipe data
• Construction data
ECDA
process
overview
Step one
Integrity Step two
preassessment Indirect
Answers the questions: inspection Step three
Is ECDA possible? Direct
Inspection tools to use? Answers the questions: examination Step four
Are there anomalies?
... and where? Answers the questions: Post
How serious are the anomalies? assessment
Data collection How good is indirect inspection? Answers the questions:
How good is the ECDA process?
Conduct inspection
Indirect tool selection Prioritize examination How often should it be made?
Identify anomalies Remaining life
Define ECDA regions Excavate & measure
Determine severity
Strength evaluation Interval assessment
Evaluate protection
Root cause analysis
Back to Step one
FIGURE 12.16 Overview of the ECDA process.